Caffeine Anhydrous: Nootropic Benefits, Side Effects & Personal Experience
As someone who is interested in nootropics, I have found that caffeine anhydrous is a popular and effective option. Caffeine anhydrous is a dehydrated form of caffeine that is often used as a stimulant and cognitive enhancer.
It is commonly found in energy drinks, pre-workout supplements, and nootropic stacks.
Caffeine anhydrous works by blocking the action of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and suppresses arousal.
By blocking adenosine, caffeine anhydrous increases the activity of other neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which can improve alertness, focus, and mood. It can also increase metabolism and fat burning, making it a popular ingredient in weight loss supplements.[1]
Overall, caffeine anhydrous can provide a number of benefits as a nootropic, including increased energy, improved mental performance, and enhanced physical endurance.
However, it is important to use it responsibly and be aware of potential side effects like anxiety, insomnia, and gastrointestinal distress. By understanding how caffeine anhydrous works and using it appropriately, it can be a valuable addition to a nootropic stack.
What is Caffeine Anhydrous?

As a nootropic enthusiast, I have come across caffeine anhydrous as a popular ingredient in many supplements. But what exactly is caffeine anhydrous?
Caffeine anhydrous is a dehydrated form of caffeine, which means it is caffeine without water. It is a highly concentrated form of caffeine that is commonly used in supplements, energy drinks, and weight loss products.
Compared to regular caffeine, caffeine anhydrous is more potent and faster-acting. It is also easier to measure and mix into products because it is a dry powder.[2]
As a nootropic, caffeine anhydrous is often used as a stimulant to increase alertness, focus, and mental energy. It is believed to work by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain, which reduces feelings of tiredness and increases wakefulness.
While caffeine anhydrous can be effective in improving cognitive performance, it is important to use it in moderation. Excessive consumption of caffeine anhydrous can lead to negative side effects such as anxiety, insomnia, and heart palpitations.
Overall, caffeine anhydrous is a dehydrated form of caffeine that is commonly used in nootropics and other supplements to enhance cognitive performance. It is a potent and fast-acting stimulant that can increase alertness, focus, and mental energy. However, it should be used in moderation to avoid negative side effects.
Mechanism of Action: How Does Caffeine Anhydrous Work?
Caffeine anhydrous is a powerful nootropic that is widely used to increase mental alertness, focus, and energy levels. As someone who has extensively researched the effects of caffeine anhydrous, I can confidently say that it is a highly effective cognitive enhancer. In this section, I will explain how caffeine anhydrous works in the brain.
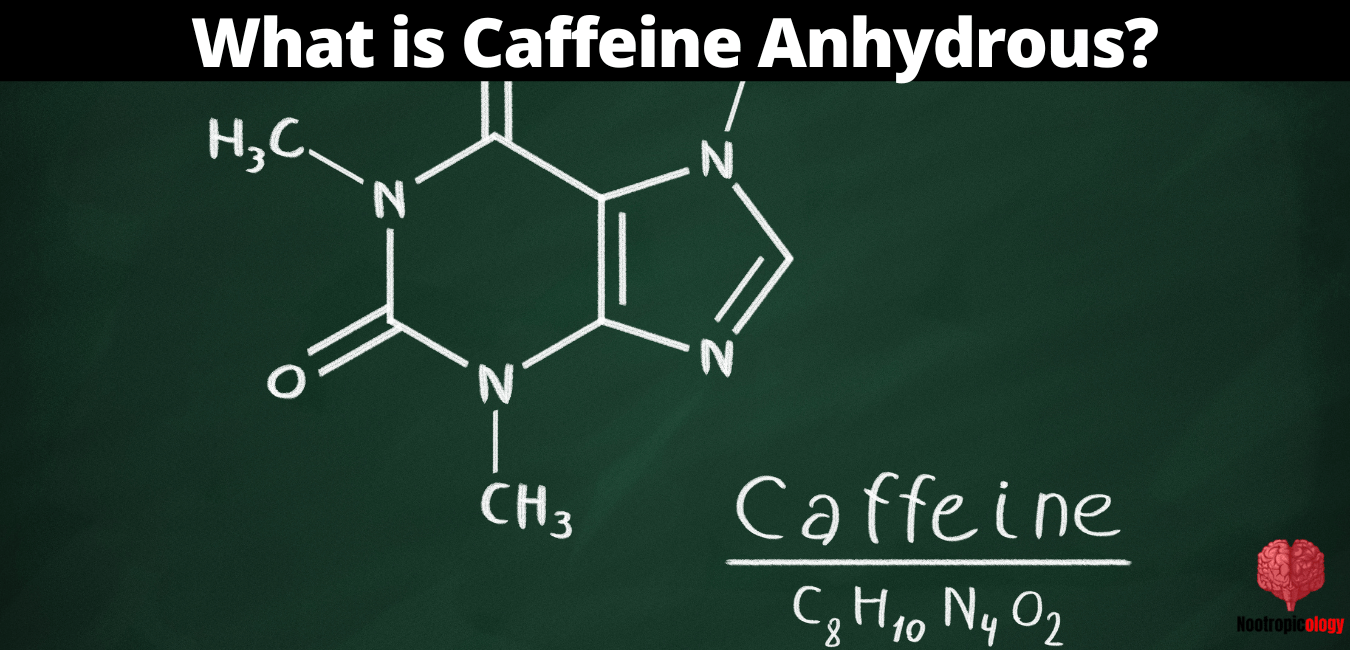
Caffeine anhydrous is a water-soluble chemical compound with the chemical formula C8H10N4O2. It is a highly purified form of caffeine that is extracted from coffee beans or tea leaves. The purity of caffeine anhydrous is typically measured using a Certificate of Analysis (COA), which provides information about the chemical composition and purity of the product.
Once caffeine anhydrous is ingested orally, it quickly enters the bloodstream and is transported to the brain. In the brain, caffeine anhydrous acts as an antagonist to adenosine receptors. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that is responsible for promoting sleep and suppressing arousal. By blocking adenosine receptors, caffeine anhydrous prevents the brain from receiving signals that promote sleepiness and fatigue.[3]
In addition to blocking adenosine receptors, caffeine anhydrous also stimulates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is associated with pleasure, motivation, and reward. This mechanism of action is what makes caffeine anhydrous such a potent cognitive enhancer. By increasing dopamine levels in the brain, caffeine anhydrous can enhance mood, motivation, and cognitive function.[4]
Overall, caffeine anhydrous is a highly effective nootropic that works by blocking adenosine receptors and stimulating the release of dopamine. Its mechanism of action makes it an excellent choice for individuals who want to improve mental alertness, focus, and energy levels.
4 Benefits of Caffeine Anhydrous
I have found that caffeine anhydrous is one of the most effective natural nootropics available.
Here are my top 4 benefits of caffeine anhydrous that make it a must-have nootropic:
1. Boosts Energy Levels
Caffeine anhydrous is a powerful stimulant that can quickly boost energy levels. It works by blocking adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and suppresses arousal. By blocking adenosine, caffeine anhydrous can help you feel more alert and awake.
2. Increases Alertness and Focus
Caffeine anhydrous is also known for its ability to increase alertness and focus. It does this by increasing the production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is associated with motivation and pleasure. By increasing dopamine levels, caffeine anhydrous can help you stay focused and motivated, even when you are feeling tired or distracted.
3. Improves Physical Performance
Caffeine anhydrous is a popular ingredient in many pre-workout supplements because of its ability to improve physical performance. It does this by increasing adrenaline levels, which can help you push through tough workouts and perform at your best.
4. Enhances Mental Clarity and Cognitive Performance
Caffeine anhydrous can also enhance mental clarity and cognitive performance. It does this by increasing blood flow to the brain, which can improve memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function.
Side Effects of Caffeine Anhydrous
As someone who has used caffeine anhydrous in high dosages, I can attest to its effectiveness in improving focus, alertness, and energy levels. That being said, it is important to note that caffeine anhydrous can also have side effects.
One of the most common side effects of caffeine anhydrous is anxiety. Caffeine is a stimulant that can increase the activity of the central nervous system (CNS), leading to feelings of restlessness and nervousness. This can be especially problematic for people who are prone to anxiety.
Another potential side effect of caffeine anhydrous is jitters or tremors. This can happen when caffeine is consumed in high doses, or when someone is particularly sensitive to its effects. These jitters can be mild or severe, and can interfere with daily activities.
Headaches are another possible side effect of caffeine anhydrous. Caffeine is a vasoconstrictor, which means it can narrow blood vessels in the brain. This can lead to headaches, especially if someone is not properly hydrated.
Insomnia is another common side effect of caffeine anhydrous. Caffeine can interfere with sleep by blocking the effects of adenosine, a chemical that promotes sleepiness. This can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to fatigue and other problems.
Heart palpitations are another potential side effect of caffeine anhydrous. Caffeine can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can be problematic for people with heart conditions or high blood pressure.
Stomach ache and nausea are also possible side effects of caffeine anhydrous. Caffeine can increase stomach acid production, leading to discomfort and even nausea in some cases.
Finally, migraines can also be a side effect of caffeine anhydrous. While caffeine can help alleviate headaches for some people, it can also trigger migraines in others.
It is important to be aware of the potential side effects of caffeine anhydrous before using it as a nootropic. While it can be an effective tool for improving focus and energy levels, it is important to use it in moderation and to be mindful of any negative effects it may have on your body.
How to Use Caffeine Anhydrous as a Nootropic (The Best Dosage)
As a nootropic, caffeine anhydrous is a popular choice for those looking to improve focus, energy, and mental performance.
That said, it is important to start with a low dose of caffeine anhydrous and gradually increase it over time. The recommended dosage is between 100-200 mg per day. However, individual tolerance levels may vary, so it is important to find the right dosage for your body.
One potential downside of caffeine anhydrous is the risk of a caffeine crash. This occurs when the effects of the caffeine wear off, leading to feelings of fatigue and lethargy. To avoid this, it is important to use caffeine anhydrous in moderation and not rely on it as a crutch.
I highly recommend using caffeine anhydrous as a part of a stack combining it with L-theanine, which I will cover more down below.
Best Caffeine Anhydrous Nootropic Stack
As someone who has been experimenting with nootropics for a while now, I have found that caffeine anhydrous is one of the most effective and reliable ingredients for boosting my focus and energy levels.
However, I have also learned that combining (or stacked) caffeine with other nootropics can enhance its effects and provide a more well-rounded cognitive boost.
In the section below, I will share my top picks for the best caffeine anhydrous nootropic stacks.
L-Theanine and Caffeine Anhydrous Stack
L-theanine is an amino acid commonly found in green tea that has been shown to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety.[5]
When combined with caffeine, it can help to smooth out the jittery effects of caffeine and provide a more focused and calm state of mind. In my experience, a 2:1 ratio of L-theanine to caffeine works best.[6]
Here are some of my favorite L-theanine and caffeine anhydrous stacks:
- Caffeine and L-Theanine Capsules: This is a simple and convenient option that can be easily found online or at your local health food store. Look for a product that contains a 2:1 ratio of L-theanine to caffeine and start with a low dose to gauge your tolerance.
- Green Tea and Coffee: If you prefer to get your caffeine and L-theanine from natural sources, drinking a cup of green tea and a cup of coffee can provide a similar effect. Just make sure to choose high-quality, organic sources to avoid any unwanted additives or pesticides.
- Vyvamind Nootropic Stack: Vyvamind contains 75 mg of Caffeine Anhydrous (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) and 6 other nootropic ingredients that work synergistically to boosts focus and overall cognition. I have used Vyvamind on and off for about 11 months now - you can read my personal review here.
Dopamine-Boosting Caffeine Anhydrous Stacks
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in motivation, reward, and pleasure. By boosting dopamine levels, caffeine anhydrous can provide a powerful cognitive boost. Here are some of my favorite dopamine-boosting caffeine anhydrous stacks:
- Caffeine and L-Tyrosine: L-tyrosine is an amino acid that is a precursor to dopamine. When combined with caffeine, it can help to increase dopamine levels and promote a more focused and motivated state of mind. Look for a product that contains a 2:1 ratio of L-tyrosine to caffeine.
- Caffeine and Rhodiola Rosea: Rhodiola Rosea is an adaptogenic herb that has been shown to increase dopamine levels and reduce fatigue. When combined with caffeine, it can provide a powerful cognitive boost. Look for a product that contains a standardized extract of Rhodiola Rosea and start with a low dose to gauge your tolerance.
In conclusion, caffeine anhydrous is a powerful nootropic ingredient that can provide a significant cognitive boost when used properly.
By combining it with other nootropics like L-theanine, L-tyrosine, and Rhodiola Rosea, you can enhance its effects and achieve a more well-rounded cognitive boost. As always, start with a low dose and work your way up to find the perfect stack for your needs.
Caffeine Anhydrous vs. Other Nootropics
I can confidently say that caffeine anhydrous is one of the most effective and widely-used nootropics out there. While it may not be as potent as some of the prescription ADHD medications or smart drugs, caffeine anhydrous is still a powerful nootropic that can provide a range of cognitive benefits.
Compared to other nootropics, caffeine anhydrous is relatively inexpensive and widely available. It is also generally considered safe when taken in moderation, although it can cause side effects like jitteriness, anxiety, and insomnia if taken in excessive amounts.
One of the main advantages of caffeine anhydrous is its ability to improve focus and alertness without the harsh side effects you see with synthetic nootropics. It can also enhance cognitive performance and memory, making it a popular supplement for students and professionals alike.
Additionally, caffeine has been shown to boost physical performance and endurance, making it a popular supplement among athletes and fitness enthusiasts.[7]
While caffeine anhydrous may not be as potent as some of the more exotic and expensive nootropics out there, it is still a great choice for anyone looking to improve their cognitive function and productivity. Whether you are a student, a professional, or an athlete, caffeine anhydrous is a versatile and effective nootropic that can help you achieve your goals.
My Personal Experience Using Caffeine Anhydrous
I have been using caffeine anhydrous as a nootropic for several months now, and I have found it to be a useful addition to my daily routine. Here are some of the benefits I experienced from my personal experience with this supplement:
- Improved focus and alertness: When I take caffeine anhydrous, I feel more awake and alert, which helps me to focus on my work and be more productive.
- Increased energy levels: Caffeine anhydrous gives me a boost of energy that helps me to power through my day without feeling tired or sluggish.
- Enhanced physical performance: I have also noticed that caffeine anhydrous can improve my physical performance during workouts, allowing me to push myself harder and achieve better results.
Of course, it's important to use caffeine anhydrous responsibly and in moderation. Too much caffeine can lead to negative side effects like jitters, anxiety, and insomnia. I always stick to the recommended dosage and avoid consuming caffeine from other sources like coffee or energy drinks when taking this supplement.
Overall, I have found caffeine anhydrous to be a helpful addition to my nootropic stack. It provides a quick and effective way to boost my focus, energy, and physical performance when I need it most.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is caffeine anhydrous stronger than caffeine?
Yes, caffeine anhydrous is a more potent form of caffeine than regular caffeine. Caffeine anhydrous is a dehydrated form of caffeine that has had all of its water removed, resulting in a more concentrated form of caffeine.
Does caffeine anhydrous help with weight loss?
Caffeine anhydrous has been shown to have a thermogenic effect, which can increase metabolism and aid in weight loss. However, it is important to note that caffeine anhydrous should not be relied upon as a sole method of weight loss and should be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and exercise.
What is the difference between caffeine anhydrous and regular caffeine?
Caffeine anhydrous is a more concentrated form of caffeine that has had all of its water removed, resulting in a more potent form of caffeine. Regular caffeine, on the other hand, is found naturally in coffee, tea, and other plants.
Does caffeine anhydrous cause sleeplessness?
Caffeine anhydrous can cause sleeplessness if taken in excessive amounts or close to bedtime. It is important to avoid consuming caffeine anhydrous too late in the day to prevent sleep disturbances.
Is caffeine anhydrous healthy?
Caffeine anhydrous can be a safe and effective supplement when used in moderation. However, it is important to note that excessive consumption of caffeine anhydrous can lead to negative side effects such as anxiety, jitters, and heart palpitations.
My Final Thoughts
After researching and analyzing the benefits and drawbacks of caffeine anhydrous as a nootropic, I have come to a few conclusions.
Firstly, caffeine anhydrous is a potent stimulant that can improve focus, alertness, and mental clarity. It can also enhance physical performance and reduce fatigue. However, it is important to note that caffeine can also cause jitters, anxiety, and insomnia in some people, especially when taken in high doses or over a long period of time.
Secondly, caffeine anhydrous is often used in combination with other nootropics to create a more well-rounded cognitive-enhancing stack. However, it is important to carefully consider the dosage and potential interactions between different substances before combining them.
Lastly, it is crucial to remember that caffeine anhydrous is not a magic pill that can instantly boost cognitive function. It is merely one tool in a larger toolbox of strategies that can help improve mental performance. Other factors such as sleep, nutrition, exercise, and stress management also play a significant role in cognitive function.
Overall, caffeine anhydrous can be a useful nootropic when used responsibly and in conjunction with other healthy lifestyle habits.
However, it is not a panacea and should be approached with caution and careful consideration.
- Ribeiro, Joaquim A, and Ana M Sebastião. “Caffeine and adenosine.” Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD vol. 20 Suppl 1 (2010): S3-15. doi:10.3233/JAD-2010-1379 ↑
- Trexler, Eric T et al. “Effects of coffee and caffeine anhydrous on strength and sprint performance.” European journal of sport science vol. 16,6 (2016): 702-10. doi:10.1080/17461391.2015.1085097 ↑
- Fredholm, Bertil B et al. “Adenosine and brain function.” International review of neurobiology vol. 63 (2005): 191-270. doi:10.1016/S0074-7742(05)63007-3 ↑
- Galvalisi, Martín et al. “Caffeine Induces a Stimulant Effect and Increases Dopamine Release in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Through the Pulmonary Inhalation Route of Administration in Rats.” Neurotoxicity research vol. 31,1 (2017): 90-98. doi:10.1007/s12640-016-9667-8 ↑
- Rao, Theertham P et al. “In Search of a Safe Natural Sleep Aid.” Journal of the American College of Nutrition vol. 34,5 (2015): 436-47. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.926153 ↑
- Owen, Gail N et al. “The combined effects of L-theanine and caffeine on cognitive performance and mood.” Nutritional neuroscience vol. 11,4 (2008): 193-8. doi:10.1179/147683008X301513 ↑
- Southward, Kyle et al. “The Effect of Acute Caffeine Ingestion on Endurance Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) vol. 48,8 (2018): 1913-1928. doi:10.1007/s40279-018-0939-8 ↑
