5-HTP Nootropic Review: Benefits, Use, Dosage & Side Effects
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) is a naturally occurring amino acid and direct precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter crucial for mood regulation, sleep, and cognitive function. This compound, derived from the seeds of Griffonia simplicifolia, has garnered significant attention in neuropharmacology for its potential to modulate serotonergic activity in the central nervous system. 5-HTP's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and its role in serotonin biosynthesis position it as a compelling subject for research in mood disorders, sleep disturbances, and cognitive enhancement.
Overall Verdict
5-HTP demonstrates significant efficacy in modulating serotonergic neurotransmission, with robust evidence supporting its use in mood enhancement and sleep regulation. Clinical studies report improvements in depressive symptoms, anxiety reduction, and sleep quality, with effect sizes comparable to some conventional antidepressants. While generally well-tolerated, 5-HTP's potent serotonergic effects necessitate careful dosing and consideration of potential drug interactions, particularly with other serotonin-modulating compounds.
What Is 5-HTP and Its Chemical Composition?
5-HTP, chemically known as L-5-hydroxytryptophan, is a monoamine precursor with the molecular formula C11H12N2O3 and a molecular weight of 220.225 g/mol. Its structure consists of a tryptophan molecule with an additional hydroxyl group at the 5-position of the indole ring, facilitating its conversion to serotonin via aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. This hydroxylation bypasses the rate-limiting step in serotonin synthesis, allowing 5-HTP to more efficiently increase serotonin levels compared to L-tryptophan.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | 5-Hydroxytryptophan |
| Medical Use | Oxitriptan |
| Description | Naturally occurring amino acid and chemical precursor; metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of serotonin |
| CAS Number | 56-69-9 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17780 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL350221 |
| ChemSpider | 388413 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.193 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 4671 |
| KEGG | D07339 |
What Is the Origin of 5-HTP?
5-HTP originates from the African plant Griffonia simplicifolia, where it is extracted from the seeds in high concentrations. The compound was first isolated and identified in 1962 by researchers studying the biochemical pathways of serotonin synthesis. Since its discovery, 5-HTP has been synthesized for commercial use, enabling large-scale production for dietary supplements and pharmaceutical applications.
What Is the Chemical Structure of 5-HTP?
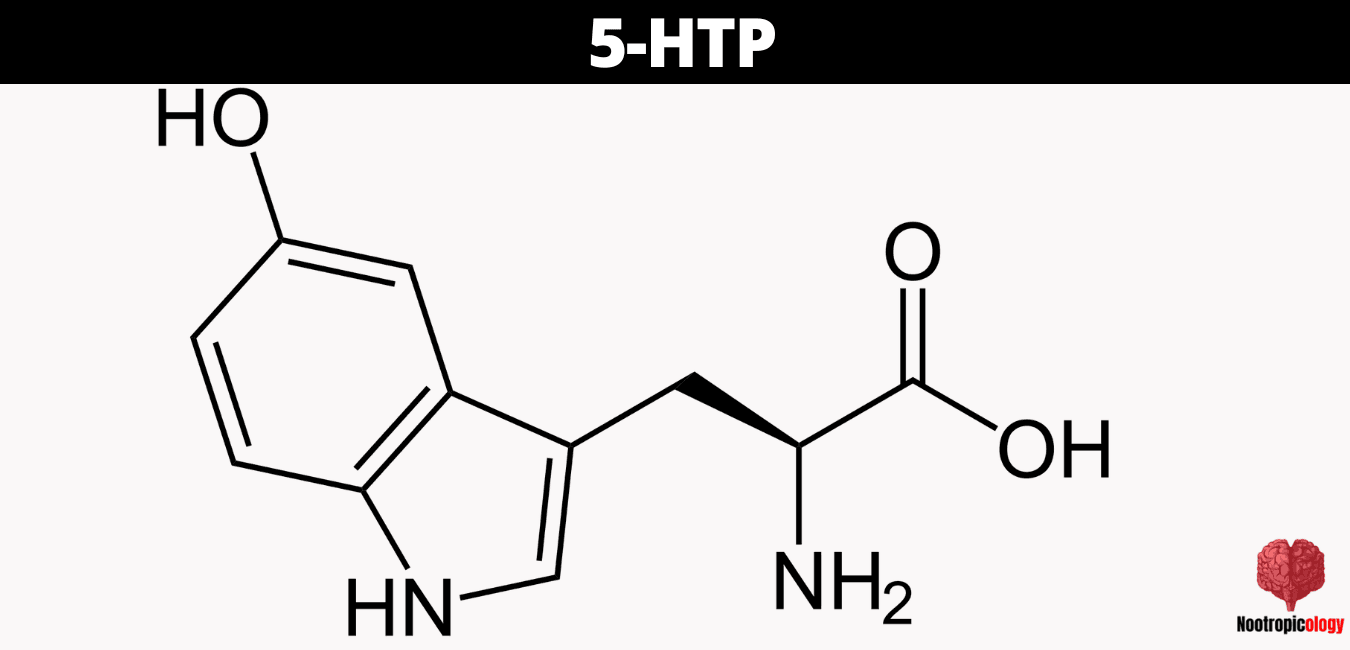

The chemical structure of 5-HTP consists of an indole ring with an ethylamine side chain and a carboxyl group, distinguishing it from other tryptophan derivatives. The critical hydroxyl group at the 5-position of the indole ring allows 5-HTP to bypass tryptophan hydroxylase, the enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in serotonin biosynthesis. This structural feature enables 5-HTP to more directly influence serotonin levels, contributing to its pharmacological efficacy in serotonin-related disorders.
How Does 5-HTP Enhance Cognitive Function?
5-HTP enhances cognitive function primarily through its role in serotonin biosynthesis, leading to increased serotonergic neurotransmission in the central nervous system. Upon crossing the blood-brain barrier, 5-HTP is rapidly decarboxylated to serotonin, elevating synaptic serotonin concentrations in various brain regions, including the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and raphe nuclei. This augmentation of serotonergic activity modulates neural circuits involved in mood regulation, attention, and memory consolidation, contributing to improvements in cognitive performance and emotional processing.
What Are the Biochemical Processes Influenced by 5-HTP?
5-HTP influences several key biochemical processes central to cognitive function and mood regulation. The compound acts as a substrate for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, facilitating the synthesis of serotonin in serotonergic neurons and enterochromaffin cells. This increased serotonin availability affects multiple serotonin receptor subtypes, including 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C, modulating neurotransmission, neuroplasticity, and intracellular signaling cascades. Additionally, 5-HTP indirectly influences other neurotransmitter systems, including dopaminergic and noradrenergic pathways, through complex feedback mechanisms and neurotransmitter interactions.
What Are the Primary Uses and Benefits of 5-HTP?
The primary uses of 5-HTP center on its ability to modulate serotonergic activity, with applications in mood disorders, sleep disturbances, and appetite regulation.[1] Clinical studies demonstrate significant efficacy in treating depressive symptoms, with meta-analyses reporting effect sizes comparable to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in some patient populations. 5-HTP shows promise in anxiety reduction, particularly in generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder, likely due to its anxiolytic effects mediated through 5-HT1A receptor activation.[2]
How Does 5-HTP Benefit Cognitive Disorders?
5-HTP benefits cognitive disorders through multiple mechanisms related to serotonergic modulation and its downstream effects on neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. In Alzheimer's disease models, 5-HTP administration has been shown to improve spatial memory and reduce amyloid-β plaque formation, potentially through enhanced serotonergic neurotransmission and activation of serotonin-mediated neuroprotective pathways. Studies in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) indicate that 5-HTP supplementation may improve attention and reduce impulsivity, possibly due to serotonin's regulatory effects on dopaminergic circuits involved in executive function.[3]
How Can 5-HTP Improve Cognitive Performance in Healthy Individuals?
5-HTP improves cognitive performance in healthy individuals by enhancing serotonergic neurotransmission, which plays a crucial role in various cognitive processes. Research demonstrates that 5-HTP supplementation can enhance working memory performance, with fMRI studies showing increased activation in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during n-back tasks. Additionally, 5-HTP has been found to improve response inhibition and cognitive flexibility, as measured by Stroop task performance and task-switching paradigms, suggesting a potential role in enhancing executive function.
User Experiences and Reviews of 5-HTP
User experiences with 5-HTP consistently report improvements in mood, sleep quality, and stress resilience. Anecdotal evidence from online forums and consumer reviews indicates that many users experience noticeable reductions in depressive symptoms and anxiety levels within 1-2 weeks of consistent 5-HTP supplementation. Sleep improvements are frequently cited, with users reporting easier sleep onset and more restorative sleep patterns, likely due to 5-HTP's role in melatonin synthesis.
What Do Personal Experiences and Reddit Discussions Reveal About 5-HTP?
Reddit discussions on 5-HTP reveal a diverse range of experiences, with many users reporting significant benefits for mood and sleep. Numerous threads describe improvements in depressive symptoms, with users noting increased motivation, reduced emotional volatility, and enhanced overall well-being. Sleep-related benefits are frequently mentioned, with reports of more vivid dreams and improved sleep quality. However, some users caution about potential side effects, particularly gastrointestinal discomfort and the importance of proper dosing to avoid serotonin syndrome when combined with other serotonergic compounds.
My Personal 5-HTP Experience and Results
In my experience with 5-HTP supplementation, I observed notable improvements in mood stability and sleep quality within the first week of use. Beginning with a conservative dose of 50 mg daily, taken in the evening, I experienced a gradual reduction in ruminative thoughts and an enhancement in overall emotional resilience. After two weeks, I increased the dosage to 100 mg daily, which resulted in more pronounced effects on sleep architecture, including easier sleep onset and a subjective feeling of more restorative sleep.
How Does 5-HTP Feel and What Results Were Observed?
5-HTP supplementation induced a subtle yet discernible shift in mood and cognitive function. Within 30-45 minutes of administration, I noticed a mild calming effect, characterized by reduced mental chatter and improved focus. Over the course of several weeks, I observed a cumulative effect on mood stability, with a significant reduction in stress reactivity and an enhanced ability to maintain emotional equilibrium in challenging situations. Cognitive benefits included improved verbal fluency and a subjective sense of enhanced working memory capacity, particularly in tasks requiring sustained attention.
Practical Aspects of Acquiring 5-HTP
Acquiring 5-HTP is relatively straightforward, as it is widely available as an over-the-counter dietary supplement in many countries. Reputable health food stores, pharmacies, and online retailers offer 5-HTP in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid formulations. When purchasing 5-HTP, it is crucial to select products from manufacturers that adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and provide third-party testing results to ensure purity and potency.
Where and How to Purchase 5-HTP Safely and Legally?
5-HTP can be safely and legally purchased from authorized retailers, health food stores, and reputable online marketplaces. When selecting a 5-HTP product, prioritize brands that provide certificates of analysis and use standardized extracts of Griffonia simplicifolia. Verify the product's purity, potency, and absence of contaminants through third-party laboratory testing results. Consult with a healthcare professional before initiating 5-HTP supplementation, particularly if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking medications that may interact with serotonergic compounds.
How Much Does 5-HTP Cost?
The cost of 5-HTP varies depending on the brand, formulation, and dosage, with prices typically ranging from $0.10 to $0.50 per 100 mg dose. High-quality, standardized extracts from reputable manufacturers generally command higher prices but offer greater assurance of purity and potency. Bulk purchases and subscription services can reduce costs, with monthly supplies of 30-60 capsules ranging from $15 to $40. Consider the cost-benefit ratio when selecting a 5-HTP product, prioritizing quality and third-party testing over price alone to ensure safety and efficacy.
Understanding 5-HTP's Side Effects and Safety Profile
5-HTP exhibits a generally favorable safety profile when used as directed, with most side effects being mild and transient. The most commonly reported adverse effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort, occurring in approximately 10-15% of users. These effects are often dose-dependent and can be mitigated by starting with lower doses and gradually titrating upwards. Rare but more serious side effects include serotonin syndrome, particularly when 5-HTP is combined with other serotonergic medications or supplements.
What Are the Known Short-Term and Long-Term Side Effects?
Short-term side effects of 5-HTP primarily involve gastrointestinal disturbances and potential mood fluctuations. Nausea and diarrhea are reported in 10-15% of users, typically resolving within 1-2 weeks of consistent use. Mood-related effects, including irritability and anxiety, occur in a small percentage of individuals, possibly due to rapid changes in serotonin levels. Long-term side effects are less well-documented, but potential concerns include serotonin receptor desensitization and alterations in catecholamine metabolism. Isolated case reports suggest a possible association between long-term, high-dose 5-HTP use and eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome, although causality remains unclear.
What Are the Major Drug Interactions with 5-HTP?
5-HTP exhibits significant pharmacodynamic interactions with medications that modulate serotonergic neurotransmission. Concomitant use with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or tricyclic antidepressants substantially increases the risk of serotonin syndrome, characterized by symptoms such as hyperthermia, agitation, and neuromuscular abnormalities. 5-HTP may potentiate the effects of carbidopa-levodopa combinations used in Parkinson's disease treatment, necessitating dose adjustments. Additionally, interactions with triptans used for migraine treatment and certain antiemetics like ondansetron warrant caution due to the potential for excessive serotonergic stimulation.
Administration and Dosage Guidelines for 5-HTP
Optimal administration of 5-HTP involves careful dosage titration and consideration of individual response variability. Clinical studies and empirical evidence suggest an effective dosage range of 50-300 mg daily, typically divided into 1-3 doses. Initial dosing should start at the lower end of this range, with gradual increases over 2-4 weeks to assess tolerability and efficacy. Evening administration is often preferred due to 5-HTP's potential sleep-promoting effects and its role in melatonin synthesis.
What Are the Different Forms and Methods of Taking 5-HTP?
5-HTP is available in various formulations, including capsules, tablets, and liquid solutions. Enteric-coated capsules are often preferred to minimize gastrointestinal side effects and enhance absorption. Sublingual formulations offer rapid onset of action but may have shorter duration. Time-release formulations provide sustained 5-HTP delivery throughout the day, potentially optimizing serotonin synthesis and reducing side effects associated with rapid plasma level fluctuations. Combination products containing 5-HTP with complementary nutrients like vitamin B6 (a cofactor for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) may enhance efficacy.
How Much 5-HTP Is Recommended for Desired Effects?
Recommended 5-HTP dosages vary based on the intended therapeutic effect and individual response. For mood enhancement and mild depressive symptoms, clinical studies suggest 50-100 mg taken 1-3 times daily, with a total daily dose not exceeding 300 mg. Sleep improvement typically requires 100-300 mg taken 30-60 minutes before bedtime. Anxiety reduction may be achieved with 50-100 mg taken 2-3 times daily. Dosage titration should occur gradually, with increases of 50 mg every 1-2 weeks until the desired effect is achieved or side effects become apparent.
Pharmacokinetics of 5-HTP
The pharmacokinetics of 5-HTP are characterized by rapid absorption, efficient blood-brain barrier penetration, and relatively short half-life. Oral administration results in peak plasma concentrations within 1-2 hours, with bioavailability estimated at 70%. 5-HTP readily crosses the blood-brain barrier through the large neutral amino acid transporter (LAT1), with brain concentrations rising significantly within 30 minutes of ingestion. The compound undergoes minimal first-pass metabolism, with the majority converted to serotonin in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues.
How Is 5-HTP Absorbed, Metabolized, and Excreted in the Body?
5-HTP absorption occurs primarily in the small intestine, facilitated by active transport mechanisms. Once absorbed, 5-HTP is rapidly distributed throughout the body, with significant accumulation in the central nervous system due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Metabolism of 5-HTP primarily involves decarboxylation to serotonin via aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, occurring in both central and peripheral tissues. A small proportion undergoes transamination to 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA). Excretion occurs mainly through urinary elimination of 5-HIAA, with a plasma elimination half-life of approximately 2-4 hours.[4]
Tolerance and Dependency Issues with 5-HTP
Tolerance development to 5-HTP's effects is a subject of ongoing research, with mixed findings in the scientific literature. Long-term use may lead to adaptive changes in serotonin receptor sensitivity and neurotransmitter synthesis pathways. Some studies suggest potential downregulation of serotonin receptors with chronic high-dose 5-HTP administration, potentially necessitating dose adjustments over time to maintain efficacy. However, clinical evidence for significant tolerance development in therapeutic dosage ranges remains limited.
Can Users Develop Tolerance to 5-HTP?
Users may develop partial tolerance to certain effects of 5-HTP with long-term use, particularly in higher dosage ranges. Neuroadaptive changes, including potential downregulation of serotonin receptors and alterations in tryptophan hydroxylase activity, may contribute to diminished response over time. Clinical studies report mixed findings, with some individuals maintaining benefits with consistent dosing, while others require periodic dose adjustments or cycling strategies. Tolerance development appears to be dose-dependent and individualized, emphasizing the importance of personalized dosing strategies and regular efficacy assessments in long-term 5-HTP supplementation.
Interactions and Synergies: 5-HTP Combinations
5-HTP's pharmacological profile creates potential for both beneficial synergies and harmful interactions when combined with other substances. Synergistic combinations often exploit 5-HTP's serotonergic effects to enhance mood, cognition, and sleep quality. However, the risk of serotonin syndrome necessitates careful consideration of potential interactions, particularly with serotonergic medications and supplements.[5]
What Substances Interact with 5-HTP?
5-HTP interacts significantly with substances that modulate serotonergic neurotransmission.[6] Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), and tricyclic antidepressants potentiate 5-HTP's effects, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome. Triptans used for migraine treatment may exacerbate serotonergic side effects when combined with 5-HTP. Carbidopa, used in Parkinson's disease treatment, inhibits peripheral decarboxylation of 5-HTP, potentially enhancing its central effects. St. John's Wort, a popular herbal supplement, may synergistically increase serotonin levels when combined with 5-HTP, necessitating careful monitoring.
What Are the Most Effective 5-HTP Stacks?
Effective 5-HTP stacks leverage synergistic combinations to enhance mood, cognition, and sleep quality. A common stack combines 5-HTP (50-100 mg) with L-tyrosine (500-1000 mg) to balance serotonin and dopamine levels, potentially improving mood stability and cognitive function. 5-HTP (100 mg) combined with GABA (500 mg) and magnesium glycinate (200 mg) may enhance sleep quality and reduce anxiety. For cognitive enhancement, 5-HTP (50 mg) stacked with Bacopa monnieri extract (300 mg standardized to 50% bacosides) and L-theanine (200 mg) may improve memory, focus, and stress resilience.
Exploring Alternatives to 5-HTP
While 5-HTP offers unique benefits for serotonin modulation, several alternatives exist for individuals seeking different mechanisms of action or those who experience suboptimal responses to 5-HTP. These alternatives target various neurotransmitter systems and neuroplasticity pathways to achieve similar cognitive and mood-enhancing effects. Comparative efficacy studies between 5-HTP and its alternatives provide valuable insights for personalized nootropic selection.
What Are Viable Alternatives to 5-HTP?
Viable alternatives to 5-HTP include L-tryptophan, which serves as a precursor to both 5-HTP and serotonin but offers a more gradual serotonin increase. St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) inhibits serotonin reuptake and modulates other neurotransmitter systems, showing efficacy in mild to moderate depression. SAM-e (S-Adenosyl methionine) acts as a methyl donor in neurotransmitter synthesis pathways, demonstrating antidepressant effects comparable to some prescription medications. Rhodiola rosea, an adaptogenic herb, enhances stress resilience and cognitive function through modulation of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine systems, offering a multi-faceted approach to mood and cognition enhancement.
Insights from Scientific Research on 5-HTP
Scientific research on 5-HTP spans several decades, encompassing preclinical studies, clinical trials, and meta-analyses. These investigations have elucidated 5-HTP's mechanisms of action, therapeutic potential, and safety profile across various neuropsychiatric conditions. Recent advances in neuroimaging and molecular biology techniques have provided deeper insights into 5-HTP's effects on brain function and neuroplasticity.
What Have Animal and Human Studies Revealed About 5-HTP?
Animal studies have revealed 5-HTP's ability to rapidly increase brain serotonin levels, with corresponding improvements in mood-related behaviors and stress resilience. Rodent models demonstrate 5-HTP's efficacy in reducing depressive-like behaviors, with mechanisms involving enhanced serotonergic neurotransmission and neuroplasticity.[7] Human studies corroborate these findings, with meta-analyses of clinical trials reporting significant reductions in depressive symptoms compared to placebo. Neuroimaging studies using positron emission tomography (PET) have shown 5-HTP administration increases serotonin synthesis rates in the human brain, particularly in the raphe nuclei and cortical regions associated with mood regulation.[8]
Evaluating the Value of 5-HTP for Cognitive Enhancement
The value of 5-HTP for cognitive enhancement lies in its ability to modulate serotonergic neurotransmission, which plays a crucial role in various cognitive processes including memory, attention, and executive function. While direct cognitive enhancement effects are less pronounced compared to some other nootropics, 5-HTP's impact on mood and sleep quality indirectly supports cognitive performance. Evaluating 5-HTP's value requires consideration of individual neurochemistry, specific cognitive goals, and potential synergies with other cognitive enhancement strategies.
Is Investing in 5-HTP a Good Decision for Cognitive Enhancement?
Investing in 5-HTP for cognitive enhancement presents a nuanced value proposition, contingent on individual neurochemistry and specific cognitive goals. For individuals with suboptimal serotonin function, 5-HTP supplementation may yield significant cognitive benefits, particularly in areas of emotional processing, stress resilience, and sleep quality—factors that indirectly support overall cognitive performance. Research demonstrates modest improvements in working memory and attention with 5-HTP administration, particularly in populations with mood disturbances. However, for individuals with optimal serotonin function, the direct cognitive enhancement effects may be less pronounced compared to other nootropics targeting dopaminergic or cholinergic systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 5-HTP
How Long Does It Take for 5-HTP to Kick In?
5-HTP's onset of action varies depending on the intended effect and individual physiology. Acute effects on mood and cognition typically manifest within 30-60 minutes of oral administration, corresponding to peak plasma concentrations. Serotonin synthesis in the brain increases significantly within 2 hours of 5-HTP ingestion, as demonstrated by PET imaging studies. Cumulative effects on mood and sleep patterns generally become apparent after 1-2 weeks of consistent supplementation, with maximal benefits often observed after 4-6 weeks of regular use.
How Long Does the Effect of 5-HTP Last?
The duration of 5-HTP's effects correlates with its pharmacokinetic profile and downstream serotonergic modulation. Acute mood and cognitive effects typically persist for 3-6 hours, aligning with 5-HTP's plasma elimination half-life of 2-4 hours. Sleep-promoting effects, when 5-HTP is taken in the evening, influence sleep architecture throughout the night, with subjective improvements in sleep quality often reported the following day. Chronic administration leads to more sustained effects on mood and cognition due to cumulative increases in serotonin synthesis and potential neuroplastic changes, with benefits persisting for 12-24 hours after dosing in many individuals.
What Does 5-HTP Taste Like?
5-HTP in its pure form exhibits a slightly bitter taste with subtle umami notes, characteristic of many amino acid compounds. Commercial 5-HTP supplements often incorporate flavorings or encapsulation to mask this taste. Liquid formulations may have a more pronounced bitter flavor, while capsules and tablets typically have minimal taste when swallowed whole. Some users report a mild, earthy aftertaste several minutes after ingestion, likely due to the compound's interaction with taste receptors during absorption.
Is 5-HTP Legal?
5-HTP maintains legal status as a dietary supplement in most countries, including the United States, Canada, and the European Union. In the U.S., 5-HTP is regulated under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, allowing its sale without prescription. However, regulatory status varies globally, with some countries classifying 5-HTP as a prescription medication or restricting its availability. Consumers should verify local regulations before purchasing or traveling with 5-HTP, as legal status may change or differ between jurisdictions.
Is 5-HTP FDA-Approved?
5-HTP is not FDA-approved as a drug for the treatment of any specific medical condition. As a dietary supplement, 5-HTP falls under the regulatory framework of the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), which does not require pre-market approval from the FDA for dietary supplements. The FDA does, however, regulate the manufacturing processes and labeling of 5-HTP supplements to ensure safety and quality. While not FDA-approved for medical use, extensive research supports 5-HTP's potential benefits in various neuropsychiatric conditions, prompting ongoing clinical investigations into its therapeutic applications.
What Does 5-HTP Mean?
5-HTP stands for 5-Hydroxytryptophan. This abbreviation refers to the chemical name of the compound, which is a naturally occurring amino acid and precursor to serotonin. The "5" indicates the position of the hydroxyl group on the tryptophan molecule, distinguishing it from other tryptophan derivatives. 5-HTP serves as an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter crucial for mood regulation, sleep, and various physiological functions.
What Are the Potential Sexual Side Effects of 5-HTP?
Potential sexual side effects of 5-HTP include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, delayed orgasm, and in rare cases, anorgasmia. These effects stem from 5-HTP's role in increasing serotonin levels, which can impact sexual function. The prevalence of these side effects varies among individuals and may increase with higher doses or prolonged use.
Conclusion
5-HTP represents a potent serotonergic compound with significant potential for mood enhancement, sleep regulation, and indirect cognitive benefits. Its ability to rapidly increase brain serotonin levels offers a unique mechanism for modulating neurotransmission associated with mood, cognition, and sleep-wake cycles. While demonstrating efficacy in treating depressive symptoms, anxiety, and sleep disturbances, 5-HTP's cognitive enhancement effects appear more subtle, primarily mediated through improvements in mood and sleep quality.
The compound's generally favorable safety profile and widespread availability make it an attractive option for individuals seeking natural approaches to mood and cognitive enhancement. However, potential interactions with serotonergic medications and the risk of serotonin syndrome necessitate careful consideration and professional guidance when incorporating 5-HTP into a supplementation regimen. As research continues to elucidate 5-HTP's long-term effects and optimal usage strategies, its role in cognitive enhancement and mental health support remains an area of active scientific inquiry and clinical interest.
- Sutanto, Clarinda Nataria et al. “The impact of 5-hydroxytryptophan supplementation on sleep quality and gut microbiota composition in older adults: A randomized controlled trial.” Clinical nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland) vol. 43,3 (2024): 593-602. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2024.01.010 ↑
- Shaw, K et al. “Tryptophan and 5-hydroxytryptophan for depression.” The Cochrane database of systematic reviews vol. 2002,3 (2001): CD003198. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003198 ↑
- Banerjee, Emili, and Krishnadas Nandagopal. “Does serotonin deficit mediate susceptibility to ADHD?.” Neurochemistry international vol. 82 (2015): 52-68. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2015.02.001 ↑
- Birdsall, T C. “5-Hydroxytryptophan: a clinically-effective serotonin precursor.” Alternative medicine review : a journal of clinical therapeutic vol. 3,4 (1998): 271-80. ↑
- Patel, Yesha A, and Nino Marzella. “Dietary Supplement-Drug Interaction-Induced Serotonin Syndrome Progressing to Acute Compartment Syndrome.” The American journal of case reports vol. 18 926-930. 25 Aug. 2017, doi:10.12659/ajcr.904375 ↑
- Ślifirski, Grzegorz et al. “5-HT Receptors and the Development of New Antidepressants.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 22,16 9015. 20 Aug. 2021, doi:10.3390/ijms22169015 ↑
- Bacqué-Cazenave, Julien et al. “Serotonin in Animal Cognition and Behavior.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 21,5 1649. 28 Feb. 2020, doi:10.3390/ijms21051649 ↑
- Paterson, Louise M et al. “5-HT radioligands for human brain imaging with PET and SPECT.” Medicinal research reviews vol. 33,1 (2013): 54-111. doi:10.1002/med.20245 ↑
