What is Taurine and How Does It Work As A Nootropic?
When it comes to health benefits, taurine is an anti-anxiety supplement that also helps you sleep better and reduces the effects of chronic tiredness.
In your brain, spinal cord, eyes, and practically every tissue in your body, taurine (2-aminoethane-sulfonic acid) is one of the most common amino acids.
Taurine is found in every part of your brain, including your retina.
For the most part, people have heard of taurine since it's a common component of infamous energy beverages like Red Bull and Rock Star.
Every now and then, there will be a report of someone dying suddenly or having a seizure after eating just three or four cans of an energy drink. Because taurine is a prominent element, many people believe taurine to be the culprit.
As it turns out, including taurine into your nootropic stack is completely risk-free. Caffeine concentration in energy drinks, which may range from 75 mg to 400 mg per can, is a problem that is often overlooked by the media.
Red Bull is a popular energy drink among everyone, from competitive athletes to soccer moms who are just trying to get through the day.
However, avoiding the sugar-laden energy drink is a better choice.
Along with a cup of coffee or green tea, take a taurine supplement as well. To get a comparable result. Absent of the drawbacks.
What is the function of taurine in the body?
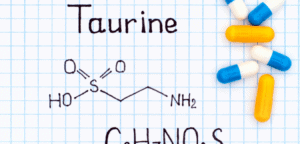

A lot of your body is made up of taurine (2-aminoethane-sulfonic acid), which is a common amino acid. The enzyme cysteine sulfenic acid decarboxylase turns methionine and cysteine into taurine in your body (CSD).
Taurine is classified as a "conditional" amino acid since your body can produce some of this amino acid. Seafood, meat, poultry, and eggs provide the remainder of your daily need for taurine, as does red meat.
Germany's Friedrich Tiedemann and Leopold Gmelin were the first to discover taurine in ox bile in 1827 and the first to extract it. A bull or an ox is what it's called in Latin, thus the name.
Many vegans and vegetarians are in danger of taurine insufficiency since it is only available in animal-based meals.
Taurine levels decrease with aging, according to research.
Possible explanation: when people age, their bodies, and brains run out of the precursors needed to make taurine.
Taurine's structure differs significantly from that of other important amino acids in two ways.
An alpha-carbon instead of a beta-carbon joins taurine's amino group. Second, unlike other amino acids, taurine's acid group is sulfonic acid rather than a carboxylic acid.
As a result of its unique structure, taurine isn't employed by your body or brain to synthesize proteins. Instead, it offers a slew of additional advantages, all of which we'll go over in further detail below.
We're learning more and more about taurine and how important it is to our health as time goes on.
Scientists in Japan were interested to see whether the advantages of taurine in animal research translated to human health.
They verified that people with the greatest amounts of taurine in their systems lived the longest using data from a WHO research that included 61 groups in 25 nations.
A powerful nootropic, taurine helps defend against Alzheimer's disease-causing beta-amyloid proteins, shield the body from environmental pollutants, and prevent mitochondrial malfunction. It also supports the inhibitory GABA system.
For long-term memory development, taurine is required for lowering inflammation in the brain, boosting the birth of new neurons, and protecting your brain from stroke-related damage.
What is the function of taurine in the brain?
Taurine helps the brain in a number of ways.
However, there are two that stick out.
- Taurine may be beneficial for those who are suffering from anxiety or depression.
If you've ever dealt with anxiety or depression, you're well aware of the toll it takes on your ability to study, work, or enjoy life in general. Taurine as a nootropic supplement may be beneficial.
Taurine has been shown to alter depression-related signaling cascades in the hippocampus, according to research.
Taurine supplementation reduced manic episodes in 121 bipolar individuals between the ages of 18 and 25 in one trial.
Taurine nootropic supplementation has been proven to be beneficial in the treatment of anxiety in a number of animal experiments.
GABA and glycine receptors in the brain are modulated. As well as reducing neurotoxicity and ensuring mitochondria do not run out of energy.
- Taurine is also a powerful anti-aging supplement.
Taurine levels decrease with aging, according to research. Taurine also seems to slow down the aging process of the brain when taken as a dietary supplement.
By reducing inflammatory processes induced by excessive iron buildup, taurine supplementation may help prevent neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
New brain cells are generated in part by taurine (neurogenesis). Taurine seems to wake up brain stem cells that have been inactive, according to research.
When things go wrong
Methionine and cysteine are building blocks of taurine, which your body makes in little amounts.
However, you'll have to make up the difference with what you eat. If you're a vegan or vegetarian, taurine deficiency is quite likely.
Conditions including diabetes, cancer, liver, kidney, and heart disease may all lead to taurine depletion.
Vitamin B6 (P-5-P), zinc, magnesium, and vitamin A deficiency are all possible causes of anemia. Likewise, consuming monosodium glutamate-containing foods (MSG).
One of the most affordable nootropic supplements is taurine, which is available for about $12 per bottle.
Add taurine to your nootropic stack if you're unsure whether or not you're receiving enough.
Advantages of taurine
Until now, you've probably never heard of taurine, the most prevalent amino acid in your body. Taurine may be the key to the world's longest-lived people, according to a growing body of studies.
According to research, taurine has the following benefits:
- Is a necessary component in the regular growth and development of the human brain
- Prevents brain cell mitochondrial malfunction
- Boosts the brain's GABA levels to protect against neurotoxicity and stress.
- lessens the likelihood of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease-causing inflammation
- Enhances neurogenesis, a process that has anti-aging benefits.
- Protects brain cells from damage caused by a stroke.
- Eliminates damage caused by beta-amyloid, which increases the risk of Alzheimer's.
- provides heavy metal and pesticide protection for brain cells
Long-term potentiation, coupled with NMDA and dopamine receptors, is required for the creation of long-term memories.
And for now, we're solely looking at the effects of taurine on the brain. This vital amino acid may also help with insulin sensitivity, diabetic problems, heart disease symptoms, fatty liver, and tinnitus.
Taurine is a nootropic that can help you live a longer, healthier, and more active life.
What is the experience of taking Taurine like?
Taurine supplementation, according to neurohackers, is an easy approach to boost energy levels.
To get a better night's sleep, try taking taurine, which is a natural sleep aid.
The majority of people who use taurine say they have better vision as a result. Less sadness and no more insulin resistance are all benefits.
Taurine has been included in several nootropic stacks to assist alleviate the symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome.
Taurine is an efficient blood pressure-lowering and atrial fibrillation-reducing supplement.
Taking taurine may be beneficial for those with ADHD
Dopamine levels in the ADHD brain's prefrontal cortex and striatum are low, according to research.
Researchers in Taiwan have discovered that large doses of taurine significantly reduced ADHD mice's hyperactivity behavior and brain activation.
In terms of dopamine transporter levels, dopamine uptake, and BDNF expression, taurine had a substantial impact.
Research into ADHD shows a substantial connection between inflammation and the condition.
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and C-reactive protein, two inflammatory cytokines, are emerging as diagnostic indicators for ADHD. Dopamine and norepinephrine are affected in the prefrontal cortex as a result of these cytokines.
Amount of Taurine You Should Take
The daily dose of taurine nootropics recommended is 500–2 gm.
Taurine should not be consumed in excess of 3 grams per day.
A good B-Complex vitamin should be used instead of an energy drink to get your taurine fix instead of relying on caffeine from coffee or tea. In the end, you'll feel better and profit from it.
Taurine is quickly absorbed and used by both the body and the brain. It is a powerful amino acid. However, research indicates that a single dosage is unlikely to have much of an impact on whether or not you experience any positive side effects.
Taurine supplementation on a regular basis for an extended period of time increases and maintains appropriate amounts of taurine in the body.
Effects of Taurine on the Body
To most individuals, taurine is well-tolerated and completely safe. And it should have no negative consequences.
If you have bipolar illness, you should avoid taking a lot of taurine since it might exacerbate your symptoms.
Buying Taurine: What to Look for
This amino acid supplement is available in powder and/capsule form.
Each taurine pill contains 500 to 1000 milligrams of supplement.
The dosage of taurine in energy drinks is too little to have any cognitive-enhancing effects. They're also laden with unhealthy chemicals like sugar, caffeine, and other additives.
In Summary
Taurine (2-aminoethane-sulfonic acid) is one of the most abundant amino acids in your body.
It's a featured ingredient in popular energy drinks like Red Bull, Rock Star, and Monster.
Taurine relieves chronic fatigue, promotes mitochondrial health, supports cellular energy, helps you sleep, and is anti-aging.
Taurine is one of the most essential substances in the human body. It plays a critical role in creating new brain cells (neurogenesis).
Supplementing with taurine seems to slow the brain aging process.
Taurine may help alleviate depression by changing depression-related signaling cascades. Taurine is the most abundant amino acid that you've ever heard of.
Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, liver disease, kidneys, or the heart can also deplete taurine.
This essential amino acid can restore insulin sensitivity, mitigate diabetic complications, reverse symptoms of heart disease, prevent and treat fatty liver, and reverse tinnitus.
Taurine is rapidly absorbed and used in your body and brain.
Recommended taurine nootropic dosage is 500 mg – 2 gm per day.
Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1 and C-reactive protein are turning out to be diagnostic markers of ADHD.
