Alpha-Lipoic Acid Nootropic Review: Benefits, Use, Dosage & Side Effects
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), a naturally occurring organosulfur compound, serves as a potent antioxidant and metabolic cofactor with significant implications for cognitive health and neuroprotection. This versatile molecule, synthesized in the mitochondria from octanoic acid, plays a crucial role in energy metabolism and exhibits unique properties that distinguish it from other antioxidants. ALA's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and its dual solubility in both water and lipid environments position it as a promising compound in the realm of cognitive enhancement and neurological health.[1]
Overall Verdict
Alpha-lipoic acid demonstrates robust neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing effects through its potent antioxidant properties and role in mitochondrial energy production. Clinical studies reveal significant improvements in cognitive function, particularly in age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. While generally well-tolerated, ALA's potential to alter glucose metabolism necessitates careful monitoring in diabetic individuals and those on glucose-lowering medications.[2]
What Is Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Its Chemical Composition?
Alpha-lipoic acid, chemically known as 1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid, is an eight-carbon dithiol compound with the molecular formula C8H14O2S2. Its structure consists of a five-membered cyclic disulfide attached to a carboxylic acid by a short hydrocarbon chain, conferring both hydrophilic and lipophilic properties. This unique chemical composition enables ALA to function in various cellular compartments, including the cytosol, plasma membrane, and extracellular space.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Common name | Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA) |
| Chemical structure | C8H14O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 206.33 g/mol |
| Solubility | Soluble in both water and lipids |
| Properties | Organosulfur compound, antioxidant, metabolic cofactor |
| Function | Potent antioxidant, mitochondrial enzyme cofactor, neuroprotective agent |
| Uses | Cognitive enhancement, neuroprotection, diabetic neuropathy treatment, antioxidant supplementation |
| Risks | Potential hypoglycemia in diabetics, rare allergic reactions, possible interactions with thyroid medications and insulin |
What Is the Origin of Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Alpha-lipoic acid originates as a naturally occurring antioxidant and enzyme cofactor synthesized in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. The endogenous production of ALA involves the enzymatic addition of sulfur to octanoic acid, catalyzed by lipoic acid synthase in the mitochondrial matrix. While ALA is produced in small quantities by the human body, dietary sources and supplementation provide significant exogenous sources of this compound.
What Is the Chemical Structure of Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
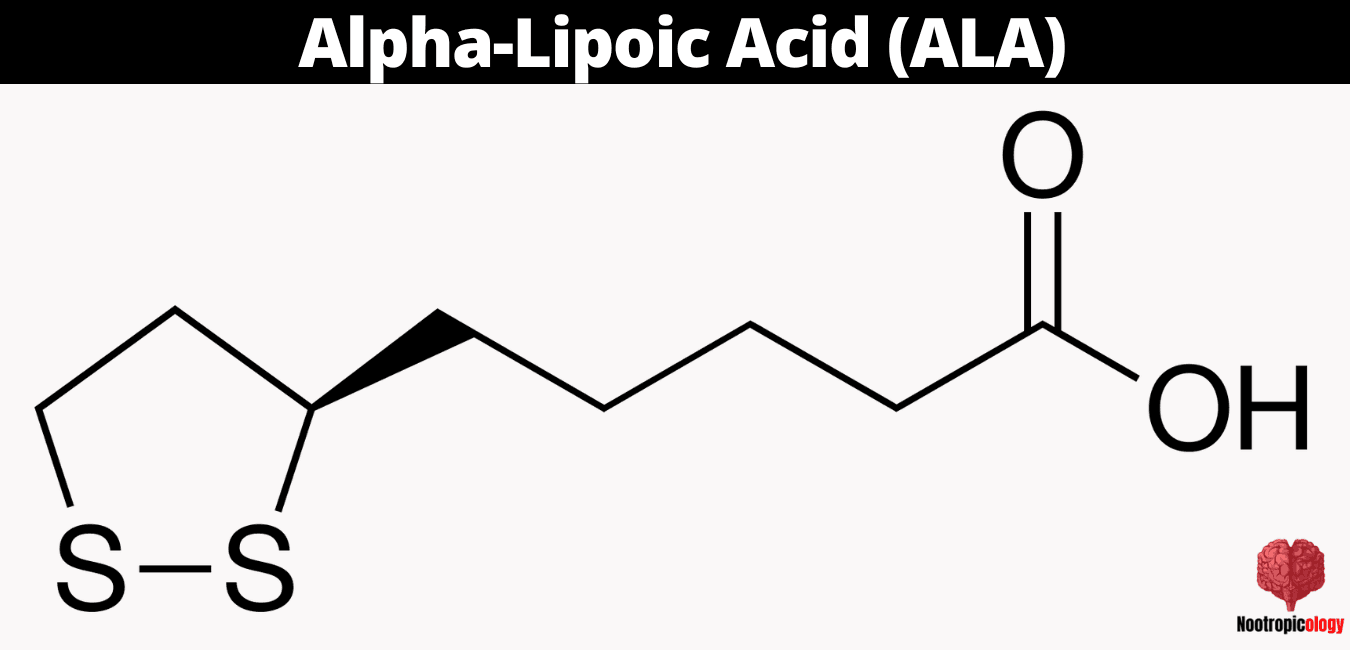

The chemical structure of alpha-lipoic acid consists of a cyclic disulfide moiety linked to a carboxylic acid group via a short alkyl chain. This unique structure results in a chiral center, with the R-enantiomer being the biologically active form naturally produced in the body. The presence of two sulfur atoms in a strained five-membered ring confers high reactivity, allowing ALA to participate in redox reactions and form intramolecular disulfide bonds.
How Does Alpha-Lipoic Acid Enhance Cognitive Function?
Alpha-lipoic acid enhances cognitive function through multiple mechanisms, primarily involving its potent antioxidant properties and role in mitochondrial energy production. ALA's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier allows it to directly scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) in neural tissues, reducing oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage. Additionally, ALA regenerates other antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, amplifying the overall antioxidant defense system in the brain.[3]
What Are the Biochemical Processes Influenced by Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Alpha-lipoic acid influences several key biochemical processes critical to cognitive function and neuroprotection. ALA serves as a cofactor for mitochondrial enzymes involved in energy metabolism, enhancing ATP production and cellular energy availability in neurons. The compound modulates glucose uptake and utilization in brain cells by activating insulin signaling pathways and glucose transporters, particularly GLUT4. ALA also exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, suppressing NF-κB activation and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production in glial cells.[4]
What Are the Primary Uses and Benefits of Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
The primary uses and benefits of alpha-lipoic acid encompass a wide range of cognitive and neurological applications. ALA supplementation demonstrates significant efficacy in improving memory, attention, and processing speed in individuals with age-related cognitive decline. Clinical studies report reduced cognitive impairment and slower progression of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease in patients receiving ALA therapy.[5] Additionally, ALA shows promise in managing diabetic neuropathy, reducing neuropathic pain and improving nerve conduction velocity.[6]
How Does Alpha-Lipoic Acid Benefit Cognitive Disorders?
Alpha-lipoic acid benefits cognitive disorders through multiple neuroprotective mechanisms. In Alzheimer's disease, ALA reduces amyloid-β plaque formation and tau hyperphosphorylation, key pathological hallmarks of the disease. ALA enhances cholinergic neurotransmission by increasing acetylcholine synthesis and release, improving cognitive symptoms in dementia patients. In Parkinson's disease, ALA protects dopaminergic neurons from oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction, potentially slowing disease progression and ameliorating motor symptoms.[7]
How Can Alpha-Lipoic Acid Improve Cognitive Performance in Healthy Individuals?
Alpha-lipoic acid improves cognitive performance in healthy individuals by enhancing mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress in the brain. ALA supplementation increases cerebral blood flow and glucose metabolism, improving energy availability for cognitive processes. Studies demonstrate enhanced memory consolidation and retrieval in healthy adults taking ALA, particularly in tasks requiring sustained attention and working memory. ALA's ability to upregulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression promotes neuroplasticity, potentially enhancing learning and cognitive flexibility.[8]
User Experiences and Reviews of Alpha-Lipoic Acid
User experiences and reviews of alpha-lipoic acid generally report positive outcomes in terms of cognitive enhancement and overall well-being. Many users describe improvements in mental clarity, focus, and memory retention after consistent ALA supplementation. Individuals with age-related cognitive concerns often report a subjective sense of "mental sharpness" and reduced brain fog. Users with neuropathic conditions frequently note reductions in pain and tingling sensations, contributing to improved quality of life.
What Do Personal Experiences and Reddit Discussions Reveal About Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Personal experiences and Reddit discussions reveal a range of reported benefits and considerations regarding alpha-lipoic acid supplementation. Users frequently report enhanced mental energy and reduced cognitive fatigue, particularly during demanding cognitive tasks or prolonged work sessions. Some individuals note improvements in glucose control and metabolism, aligning with ALA's known effects on insulin sensitivity. Discussions often highlight the importance of consistent use and appropriate dosing, with some users reporting optimal results when combining ALA with other antioxidants or B-complex vitamins.
My Personal Alpha-Lipoic Acid Experience and Results
My personal experience with alpha-lipoic acid supplementation yielded noticeable improvements in cognitive function and overall energy levels. After four weeks of daily 600 mg ALA intake, I observed enhanced mental clarity and improved ability to sustain focus during complex problem-solving tasks. Subjectively, I experienced a reduction in mental fatigue during prolonged work sessions, allowing for more consistent cognitive performance throughout the day. Additionally, I noticed a subtle improvement in short-term memory recall, particularly in remembering numerical sequences and technical details.
How Does Alpha-Lipoic Acid Feel and What Results Were Observed?
Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation produces a subtle yet discernible enhancement in cognitive acuity and mental energy. The effects manifest gradually, with peak cognitive benefits typically observed after 2-3 weeks of consistent use. I experienced improved information processing speed, evidenced by faster comprehension of complex texts and more efficient decision-making in time-sensitive situations. Notably, the cognitive enhancements were accompanied by a general sense of well-being and reduced mental fatigue, suggesting ALA's potential impact on overall brain health and function.
Practical Aspects of Acquiring Alpha-Lipoic Acid
Alpha-lipoic acid is widely available as a dietary supplement in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders. Reputable health food stores, pharmacies, and online retailers offer ALA supplements from numerous manufacturers. When selecting an ALA product, prioritize those from established brands that adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and provide third-party testing for purity and potency. Consider products that combine ALA with complementary antioxidants or B vitamins for potential synergistic effects.
Where and How to Purchase Alpha-Lipoic Acid Safely and Legally?
Alpha-lipoic acid can be purchased safely and legally from authorized supplement retailers, pharmacies, and reputable online marketplaces. Ensure the chosen supplier provides detailed product information, including ALA concentration, recommended dosage, and any additional ingredients. Verify the manufacturer's credibility through certifications from recognized organizations such as NSF International or USP. For international purchases, confirm compliance with local regulations regarding dietary supplement importation and distribution to ensure legal acquisition.
How Much Does Alpha-Lipoic Acid Cost?
Alpha-lipoic acid supplements vary in cost depending on factors such as brand, dosage, and formulation. Typical price ranges for a month's supply (30-60 capsules) of ALA range from $15 to $40 USD. Higher-priced options often include additional antioxidants or specialized delivery systems. Bulk purchases or subscription services may offer cost savings. Consider the cost per serving and ALA concentration when comparing products to determine the most economical option without compromising quality.
Understanding Alpha-Lipoic Acid's Side Effects and Safety Profile
Alpha-lipoic acid demonstrates a favorable safety profile with minimal reported adverse effects in clinical studies. Common side effects, when they occur, are generally mild and may include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, or skin rash. ALA's ability to lower blood glucose levels necessitates careful monitoring in diabetic individuals to prevent hypoglycemia. Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions have been reported, emphasizing the importance of starting with lower doses and gradually increasing as tolerated.
What Are the Known Short-Term and Long-Term Side Effects?
Short-term side effects of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation may include transient gastrointestinal disturbances, headaches, or mild skin itching. These effects typically resolve with continued use or dose adjustment. Long-term studies on ALA supplementation are limited, but available data suggest no significant adverse effects with prolonged use at recommended dosages. Theoretical concerns exist regarding potential thyroid hormone disruption with high-dose, long-term ALA use, warranting periodic thyroid function monitoring in susceptible individuals.
What Are the Major Drug Interactions with Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Alpha-lipoic acid exhibits significant interactions with medications that affect blood glucose levels, particularly insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents. Concurrent use may potentiate hypoglycemic effects, necessitating careful blood glucose monitoring and potential dose adjustments. ALA may enhance the effects of antihypertensive medications, potentially leading to excessive blood pressure reduction. Interactions with thyroid hormones and levothyroxine have been reported, potentially altering thyroid function tests and requiring dose adjustments. Concomitant use of ALA with chelating agents or heavy metal-containing supplements may alter metal excretion patterns.
Administration and Dosage Guidelines for Alpha-Lipoic Acid
Alpha-lipoic acid administration requires careful consideration of dosage, timing, and individual factors to optimize its cognitive-enhancing and neuroprotective effects. Recommended dosages typically range from 300 mg to 600 mg daily for cognitive health, with higher doses up to 1200 mg used in clinical studies for specific neurological conditions. ALA absorption improves when taken on an empty stomach, ideally 30 minutes before meals. For individuals sensitive to gastrointestinal effects, dividing the daily dose into two or three administrations may improve tolerability.
What Are the Different Forms and Methods of Taking Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Alpha-lipoic acid is available in various forms, each with specific considerations for administration. Oral capsules and tablets represent the most common and convenient method of supplementation, offering precise dosing and ease of use. Powder formulations allow for flexible dosing and can be mixed with liquids, though they may have a bitter taste. Intravenous ALA administration, used primarily in clinical settings, provides rapid bioavailability and is employed for acute treatment of diabetic neuropathy. Novel delivery systems, such as liposomal formulations, aim to enhance ALA absorption and bioavailability through improved cellular uptake.
How Much Alpha-Lipoic Acid Is Recommended for Desired Effects?
The recommended dosage of alpha-lipoic acid varies based on the intended therapeutic effect and individual factors. For general cognitive enhancement and antioxidant support, doses of 300-600 mg daily have demonstrated efficacy in clinical studies. Higher doses of 600-1200 mg daily are often employed in the management of diabetic neuropathy and neurodegenerative disorders. Cognitive performance improvements in healthy adults have been observed with doses ranging from 400-600 mg daily. Individual response may vary, necessitating personalized dosing strategies based on clinical response and tolerability.
Pharmacokinetics of Alpha-Lipoic Acid
Alpha-lipoic acid exhibits complex pharmacokinetics characterized by rapid absorption, extensive metabolism, and relatively short plasma half-life. Oral ALA administration results in peak plasma concentrations within 30-60 minutes, reflecting rapid gastrointestinal absorption. The compound undergoes significant first-pass metabolism in the liver, with various metabolites contributing to its biological effects. ALA demonstrates non-linear pharmacokinetics, with bioavailability decreasing at higher doses due to saturation of absorption mechanisms.
How Is Alpha-Lipoic Acid Absorbed, Metabolized, and Excreted in the Body?
Alpha-lipoic acid absorption occurs primarily in the small intestine, facilitated by both passive diffusion and active transport mechanisms. Upon entering the bloodstream, ALA binds extensively to plasma proteins, with only a small fraction remaining in the free form. Hepatic metabolism of ALA involves reduction to dihydrolipoic acid and various oxidative pathways, producing metabolites such as bisnorlipoic acid and tetranorlipoic acid. Renal excretion represents the primary route of elimination for ALA and its metabolites, with urinary recovery accounting for approximately 80% of the administered dose within 24 hours.
Tolerance and Dependency Issues with Alpha-Lipoic Acid
Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation does not typically lead to tolerance or dependency issues when used at recommended dosages. Long-term studies have not demonstrated significant decreases in efficacy or requirements for dose escalation to maintain cognitive benefits. The compound's role as an endogenous antioxidant and metabolic cofactor suggests a low potential for physiological dependence. However, abrupt discontinuation after prolonged high-dose supplementation may theoretically result in temporary reductions in antioxidant capacity, emphasizing the importance of gradual dose tapering if cessation is desired.
Can Users Develop Tolerance to Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Users do not typically develop tolerance to alpha-lipoic acid in the context of its cognitive-enhancing and neuroprotective effects. The compound's mechanisms of action, primarily involving antioxidant functions and mitochondrial support, are not associated with receptor desensitization or downregulation that commonly lead to tolerance development. Long-term studies have demonstrated sustained benefits with consistent ALA supplementation, suggesting that its effects remain stable over time. Individual variations in response may occur due to factors such as oxidative stress levels and overall health status rather than tolerance development.
Interactions and Synergies: Alpha-Lipoic Acid Combinations
Alpha-lipoic acid exhibits potential synergistic effects when combined with other antioxidants and neuroprotective compounds. Combinations with acetyl-L-carnitine have shown enhanced mitochondrial function and cognitive benefits compared to either compound alone. ALA synergizes with omega-3 fatty acids, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), in reducing neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Co-administration with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) potentiates glutathione synthesis, enhancing cellular antioxidant defenses. Careful consideration of potential interactions is necessary when combining ALA with other supplements or medications.
What Substances Interact with Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Alpha-lipoic acid interacts with various substances, necessitating careful consideration in supplementation regimens. ALA enhances the effects of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents, potentially leading to hypoglycemia in diabetic individuals. Concurrent use with antihypertensive medications may result in additive blood pressure-lowering effects. ALA interacts with thyroid hormones, potentially altering thyroid function tests and requiring dose adjustments of thyroid medications. The compound may enhance the effects of other antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, potentially allowing for lower doses of these nutrients when used in combination.
What Are the Most Effective Alpha-Lipoic Acid Stacks?
Effective alpha-lipoic acid stacks leverage synergistic combinations to enhance cognitive function and neuroprotection. ALA combined with acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) in a 1:1 ratio (typically 300-600 mg each) demonstrates superior mitochondrial support and cognitive enhancement compared to either compound alone. A stack of ALA (300-600 mg) with omega-3 fatty acids (1-2 g DHA/EPA) and coenzyme Q10 (100-200 mg) provides comprehensive antioxidant and neuroprotective benefits. For enhanced glutathione production, combining ALA (300-600 mg) with N-acetylcysteine (600-1200 mg) and glycine (2-3 g) supports cellular detoxification and antioxidant defense. These stacks should be tailored to individual needs and health status, with dosages adjusted based on clinical response and tolerability.
Exploring Alternatives to Alpha-Lipoic Acid
While alpha-lipoic acid offers unique benefits, several alternatives exist for cognitive enhancement and neuroprotection. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) serves as a powerful antioxidant and precursor to glutathione, offering similar neuroprotective effects. Coenzyme Q10 supports mitochondrial function and energy production in neurons, complementing ALA's metabolic effects. Resveratrol, a polyphenol compound, demonstrates potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties in the central nervous system. These alternatives may be considered based on individual response, specific health goals, and potential contraindications.
What Are Viable Alternatives to Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Viable alternatives to alpha-lipoic acid include compounds with similar antioxidant and neuroprotective profiles. Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) supports mitochondrial function and neurotransmitter synthesis, offering cognitive benefits particularly in age-related decline. Phosphatidylserine, a phospholipid compound, enhances cognitive function by supporting neuronal membrane integrity and neurotransmitter signaling. Ginkgo biloba extract improves cerebral blood flow and demonstrates antioxidant properties, potentially enhancing cognitive performance. These alternatives may be used individually or in combination, depending on specific cognitive goals and individual response.
Insights from Scientific Research on Alpha-Lipoic Acid
Scientific research on alpha-lipoic acid reveals its multifaceted effects on cognitive function and neuroprotection. Preclinical studies demonstrate ALA's ability to attenuate oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage and enhance mitochondrial function in various brain regions. Clinical trials have shown significant improvements in cognitive performance, particularly in memory and attention tasks, in both healthy adults and individuals with mild cognitive impairment. ALA's potential in neurodegenerative disorders is supported by studies showing reduced amyloid-β accumulation and improved cognitive outcomes in Alzheimer's disease patients.
What Have Animal and Human Studies Revealed About Alpha-Lipoic Acid?
Animal studies have elucidated alpha-lipoic acid's neuroprotective mechanisms, including enhanced antioxidant enzyme activity and reduced lipid peroxidation in brain tissues. Rodent models of neurodegenerative diseases demonstrate ALA's ability to improve cognitive performance and reduce pathological markers such as amyloid-β plaques. Human studies reveal significant improvements in cognitive function scores and reduced progression of cognitive decline in elderly subjects receiving ALA supplementation. Clinical trials in diabetic neuropathy patients show ALA's efficacy in reducing neuropathic pain and improving nerve conduction velocity, highlighting its potential in peripheral nerve disorders.
Evaluating the Value of Alpha-Lipoic Acid for Cognitive Enhancement
Alpha-lipoic acid demonstrates significant value for cognitive enhancement, particularly in the context of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. Its unique antioxidant properties, coupled with its role in mitochondrial energy production, position ALA as a versatile compound for supporting brain health. Clinical evidence supports its efficacy in improving memory, attention, and processing speed, with a favorable safety profile at recommended dosages. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and regenerate other antioxidants enhances its value in comprehensive neuroprotective strategies.
Is Investing in Alpha-Lipoic Acid a Good Decision for Cognitive Enhancement?
Investing in alpha-lipoic acid for cognitive enhancement represents a scientifically supported decision, particularly for individuals seeking to maintain cognitive function with age or manage specific neurological conditions. The compound's well-established safety profile and multiple mechanisms of action provide a robust foundation for its use in cognitive health regimens. ALA's potential to synergize with other neuroprotective compounds offers flexibility in tailoring supplementation strategies to individual needs. While individual responses may vary, the cumulative evidence suggests that ALA supplementation can yield significant cognitive benefits when used consistently and appropriately.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Alpha-Lipoic Acid
How Long Does It Take for Alpha-Lipoic Acid to Kick In?
Alpha-lipoic acid's acute effects on glucose metabolism and antioxidant activity begin within 30-60 minutes of oral administration. Cognitive benefits typically emerge gradually, with noticeable improvements in mental clarity and focus often reported within 2-3 weeks of consistent supplementation. Maximal cognitive enhancement effects may require 4-8 weeks of regular use, reflecting the compound's cumulative neuroprotective actions and potential neuroplastic changes. Individual response times vary based on factors such as dosage, overall health status, and concurrent lifestyle modifications.
How Long Does the Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid Last?
The duration of alpha-lipoic acid's effects varies depending on the specific physiological parameter being considered. Acute antioxidant effects persist for 3-5 hours following a single dose, corresponding to the compound's plasma half-life. Metabolic effects on glucose utilization may last 6-8 hours post-administration. Cognitive enhancement effects from consistent supplementation typically persist throughout the day with regular dosing, reflecting ALA's cumulative neuroprotective actions. Long-term neuroprotective benefits may extend beyond the supplementation period due to sustained improvements in mitochondrial function and reduced oxidative damage.
What Does Alpha-Lipoic Acid Taste Like?
Alpha-lipoic acid in its pure form exhibits a distinct, slightly sulfurous taste with bitter undertones. Encapsulated or tablet forms generally mask this taste, providing a neutral sensory experience. Powder formulations may present the characteristic taste, which some users describe as metallic or acidic. Flavored ALA supplements are available, incorporating masking agents to improve palatability. The taste, when present, serves as an indicator of the compound's potency and purity, reflecting its sulfur-containing molecular structure.
Is Alpha-Lipoic Acid Legal?
Alpha-lipoic acid is legal and widely available as a dietary supplement in most countries, including the United States, European Union member states, and Canada. It is classified as a non-prescription supplement and can be purchased over-the-counter without restrictions. Some countries may regulate ALA as a pharmaceutical when used in specific medical contexts, such as the treatment of diabetic neuropathy. Consumers should verify local regulations regarding dietary supplement importation and use, particularly when purchasing from international sources or for therapeutic applications.
Is Alpha-Lipoic Acid FDA-Approved?
Alpha-lipoic acid is not FDA-approved as a drug for specific medical indications in the United States. However, it is recognized as a dietary supplement under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This classification allows ALA to be marketed and sold as a supplement without requiring FDA approval, provided manufacturers comply with good manufacturing practices and do not make specific disease treatment claims. In some European countries, ALA is approved as a prescription medication for diabetic neuropathy, reflecting its therapeutic potential in certain medical contexts.
Conclusion
Alpha-lipoic acid emerges as a promising compound for cognitive enhancement and neuroprotection, supported by a robust body of scientific evidence. Its unique antioxidant properties, coupled with its role in mitochondrial energy production, position ALA as a versatile tool in the pursuit of optimal brain health. Clinical studies demonstrate significant improvements in cognitive function, particularly in memory, attention, and processing speed, with potential applications in both healthy individuals and those with neurological disorders. The compound's favorable safety profile and synergistic potential with other neuroprotective agents further enhance its value in comprehensive cognitive health strategies.
While individual responses may vary, the cumulative evidence suggests that ALA supplementation can yield tangible cognitive benefits when used consistently and appropriately. As research continues to elucidate ALA's mechanisms of action and long-term effects, its role in cognitive enhancement and neuroprotection is likely to expand. Users considering ALA supplementation should consult with healthcare professionals to determine appropriate dosing and integration into their overall health regimen, particularly in the context of existing medical conditions or medication use. With careful consideration and informed use, alpha-lipoic acid offers a promising avenue for supporting cognitive function and brain health across the lifespan.
- Packer, L et al. “Neuroprotection by the metabolic antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid.” Free radical biology & medicine vol. 22,1-2 (1997): 359-78. doi:10.1016/s0891-5849(96)00269-9 ↑
- Capece, Umberto et al. “Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Glucose Metabolism: A Comprehensive Update on Biochemical and Therapeutic Features.” Nutrients vol. 15,1 18. 21 Dec. 2022, doi:10.3390/nu15010018 ↑
- Maciejczyk, Mateusz et al. “α-Lipoic Acid Strengthens the Antioxidant Barrier and Reduces Oxidative, Nitrosative, and Glycative Damage, as well as Inhibits Inflammation and Apoptosis in the Hypothalamus but Not in the Cerebral Cortex of Insulin-Resistant Rats.” Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity vol. 2022 7450514. 29 Mar. 2022, doi:10.1155/2022/7450514 ↑
- Ying, Zhekang et al. “Evidence that α-lipoic acid inhibits NF-κB activation independent of its antioxidant function.” Inflammation research : official journal of the European Histamine Research Society ... [et al.] vol. 60,3 (2011): 219-25. doi:10.1007/s00011-010-0256-7 ↑
- Hager, K et al. “Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Alzheimer's disease--a 48 months follow-up analysis.” Journal of neural transmission. Supplementum ,72 (2007): 189-93. doi:10.1007/978-3-211-73574-9_24 ↑
- Vallianou, Natalia et al. “Alpha-lipoic Acid and diabetic neuropathy.” The review of diabetic studies : RDS vol. 6,4 (2009): 230-6. doi:10.1900/RDS.2009.6.230 ↑
- Zhang, Yan-Hui et al. “α-Lipoic acid improves abnormal behavior by mitigation of oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis, and tauopathy in P301S Tau transgenic mice.” Redox biology vol. 14 (2018): 535-548. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.001 ↑
- Zhang, Yan-Hui et al. “α-Lipoic Acid Maintains Brain Glucose Metabolism via BDNF/TrkB/HIF-1α Signaling Pathway in P301S Mice.” Frontiers in aging neuroscience vol. 12 262. 21 Aug. 2020, doi:10.3389/fnagi.2020.00262 ↑
