Choline Nootropic Review: Benefits, Use, Dosage & Side Effects
Choline stands as an essential nutrient critical for neurotransmitter synthesis, cell membrane integrity, and neural signaling through its role as a precursor to acetylcholine (ACh) and phosphatidylcholine. This water-soluble compound directly influences synaptic plasticity, memory formation, and cognitive processing through its participation in cholinergic neurotransmission and membrane phospholipid synthesis. The brain's dependence on adequate choline supplies for optimal function highlights its significance in cognitive enhancement and neuroprotection.[1]
Overall Verdict
Choline supplementation demonstrates robust cognitive enhancement effects through optimization of acetylcholine synthesis and membrane phospholipid production in neural tissues. The compound's efficacy manifests most prominently in memory formation, attention, and cognitive processing speed, with optimal dosing proving crucial for maximizing benefits. Clinical evidence supports choline's cognitive-enhancing properties across diverse populations, though individual response patterns necessitate personalized dosing strategies.
What Is Choline and Its Chemical Composition?
Choline exists as a quaternary ammonium compound with the molecular formula C5H14NO, characterized by its trimethylamine structure and hydroxyl group. The molecule's chemical properties enable its essential roles in neurotransmitter synthesis and membrane phospholipid formation through specific enzymatic pathways. Choline's structure facilitates its transport across the blood-brain barrier through dedicated choline transporters, ensuring delivery to neural tissues.
| Property | Information |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | 2-Hydroxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium |
| Chemical formula | [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+ |
| Molar mass | 104.173 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 62-49-7 |
| Appearance | Viscous colorless deliquescent liquid (as hydroxide) |
| Solubility | Very soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, insoluble in diethyl ether and chloroform |
| Biological role | Essential nutrient, precursor to acetylcholine and phospholipids |
| Dietary sources | Organ meats, egg yolks, dairy products, peanuts, beans, nuts, seeds |
| Deficiency effects | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, muscle damage |
| Excess effects | Low blood pressure, sweating, diarrhea, fish-like body odor |
| Biosynthesis | Can be synthesized from ethanolamine via methylation |
| Metabolism | Involved in one-carbon metabolism and lipid transport |
What Is the Origin of Choline?
Choline originates both from dietary sources and endogenous synthesis through methylation of phosphatidylethanolamine in liver tissue. The compound's presence in food sources varies significantly, with highest concentrations found in egg yolks, liver, and soybeans. Endogenous production capabilities prove insufficient for optimal cognitive function, necessitating dietary intake or supplementation for maintaining adequate choline status.
What Is the Chemical Structure of Choline?
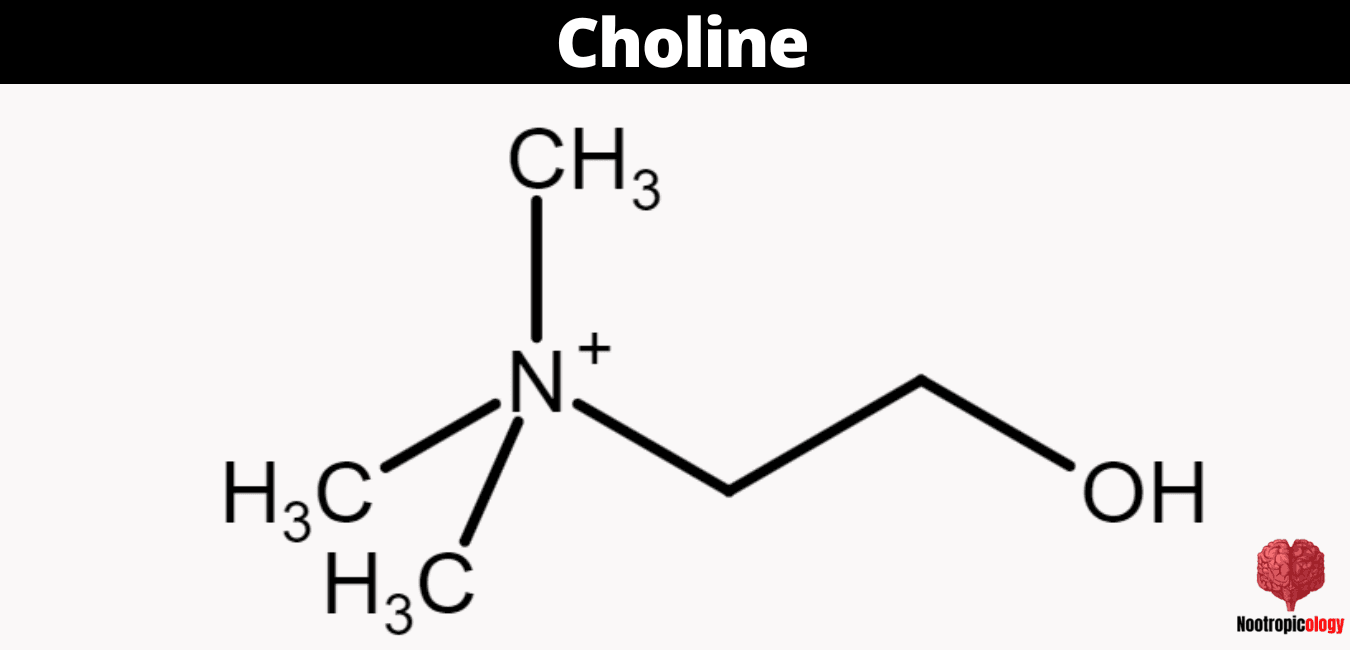

Choline's molecular architecture centers on a positively charged nitrogen atom bonded to three methyl groups and an ethanol moiety. The compound's quaternary ammonium structure enables its function as a precursor to acetylcholine through enzymatic acetylation of the hydroxyl group. This unique chemical composition facilitates choline's role in phospholipid synthesis through incorporation into phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin.
How Does Choline Enhance Cognitive Function?
Choline enhances cognitive function through direct augmentation of acetylcholine synthesis in cholinergic neurons throughout the brain. The compound's conversion to phosphatidylcholine supports membrane fluidity and signal transduction in neural tissues, optimizing synaptic transmission. Enhanced cholinergic signaling results in improved memory formation, attention, and cognitive processing speed through activation of nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.[2]
What Are the Biochemical Processes Influenced by Choline?
Choline influences multiple biochemical pathways central to cognitive function, including acetylcholine synthesis through choline acetyltransferase activity in cholinergic neurons. The compound's incorporation into membrane phospholipids affects membrane fluidity, receptor function, and signal transduction efficiency across neural networks. Methylation processes utilizing choline-derived methyl groups impact gene expression patterns and neurotransmitter metabolism throughout the central nervous system.[3]
What Are the Primary Uses and Benefits of Choline?
Choline supplementation primarily enhances memory formation, attention span, and cognitive processing speed through optimization of cholinergic neurotransmission. The compound's benefits extend to neuroprotection through maintenance of membrane integrity and reduction of homocysteine levels via methyl donation pathways. Cognitive enhancement effects manifest across multiple domains, including verbal memory, spatial cognition, and executive function.[4]
How Does Choline Benefit Cognitive Disorders?
Choline supplementation demonstrates significant efficacy in treating cognitive decline associated with cholinergic deficiency states and age-related memory impairment. The compound's role in membrane repair and acetylcholine synthesis supports cognitive recovery in various neurological conditions affecting cholinergic function. Enhanced synaptic plasticity and neuronal membrane integrity contribute to cognitive rehabilitation outcomes.
How Can Choline Improve Cognitive Performance in Healthy Individuals?
Choline optimizes cognitive performance in healthy individuals through enhancement of acetylcholine synthesis and improved neural membrane function. The compound's effects on synaptic transmission and neural circuit efficiency result in measurable improvements in memory consolidation and recall. Enhanced cholinergic signaling supports sustained attention and mental clarity during complex cognitive tasks.[5]
User Experiences and Reviews of Choline
User reports consistently describe improvements in memory recall, mental clarity, and focus duration following choline supplementation. Cognitive benefits typically manifest within 30-60 minutes of administration, with effects lasting 4-6 hours depending on the specific form of choline utilized. The most pronounced improvements occur in tasks requiring sustained attention and memory consolidation, particularly during periods of high cognitive demand.
What Do Personal Experiences and Reddit Discussions Reveal About Choline?
Online community discussions reveal consistent patterns of enhanced cognitive performance following choline supplementation, particularly with alpha-GPC and CDP-choline forms. Users report optimal results when combining choline sources with racetams or other nootropics that increase acetylcholine utilization. Experiential reports emphasize the importance of individual dosage optimization, with some users requiring adjustment periods to find their optimal supplementation protocol.
My Personal Choline Experience and Results
My initial supplementation with CDP-choline produced noticeable improvements in verbal fluency and working memory capacity within the first week of consistent use. The cognitive enhancement effects manifested most prominently during tasks requiring sustained focus and information processing, with reduced mental fatigue as a secondary benefit. Regular supplementation established a baseline of improved cognitive function, particularly in areas of memory consolidation and recall speed.
How Does Choline Feel and What Results Were Observed?
Choline supplementation produces distinct improvements in mental clarity and cognitive stamina, characterized by enhanced focus duration and reduced cognitive fatigue. The effects present as a clean, natural enhancement of cognitive capabilities rather than a stimulatory effect, with improved information processing and memory recall. Sustained supplementation results in cumulative benefits for cognitive function, particularly in areas of verbal memory and executive processing.
Practical Aspects of Acquiring Choline
High-quality choline supplements come in multiple forms, including alpha-GPC, CDP-choline (citicoline), and choline bitartrate, each offering distinct bioavailability profiles. Product selection criteria include purity verification, standardized content analysis, and third-party testing documentation. Manufacturing standards and quality control measures ensure consistent potency and minimal contaminant presence.
Where and How to Purchase Choline Safely and Legally?
Choline supplements undergo regulation as dietary supplements, available through established retail channels and specialized nootropic vendors. Quality assurance measures include certificate of analysis documentation and third-party laboratory testing verification. Procurement through reputable suppliers ensures product authenticity and adherence to manufacturing standards.
How Much Does Choline Cost?
Choline supplementation presents varying cost profiles depending on the specific form selected, with alpha-GPC commanding premium pricing due to higher bioavailability. Monthly supplementation costs range from $20-60 based on dosage requirements and chosen choline form. The investment-to-benefit ratio favors high-quality choline sources despite higher initial costs, given their superior bioavailability and cognitive enhancement effects.
Understanding Choline's Side Effects and Safety Profile
Choline supplementation carries specific considerations regarding dosage optimization and potential cholinergic side effects at higher doses. Monitoring individual response patterns ensures optimal supplementation without risking cholinergic oversaturation symptoms. The compound's safety profile supports long-term supplementation within established dosing guidelines.
What Are the Known Short-Term and Long-Term Side Effects?
Acute excessive choline intake manifests through cholinergic symptoms including headache, nausea, and gastrointestinal discomfort. Long-term supplementation at appropriate doses demonstrates excellent safety profiles without significant adverse effects. Individual sensitivity variations necessitate personalized dosing protocols to minimize side effect risk while maximizing cognitive benefits.[6]
What Are the Major Drug Interactions with Choline?
Choline exhibits interactions with parasympathomimetic medications and anticholinergic drugs through its effects on cholinergic neurotransmission. Concurrent use of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors requires careful dosing consideration due to potential cholinergic system oversaturation. Certain psychiatric medications affecting cholinergic function necessitate adjusted choline supplementation protocols.
Administration and Dosage Guidelines for Choline
Optimal choline dosing ranges from 250-1000mg daily depending on the specific form utilized and individual response patterns. Administration timing favors morning dosing with food for enhanced absorption and reduced gastrointestinal effects. Dose titration starting at lower ranges allows for assessment of individual response and minimizes potential side effects.
What Are the Different Forms and Methods of Taking Choline?
Choline supplementation options include alpha-GPC, CDP-choline, choline bitartrate, and phosphatidylcholine, each presenting distinct bioavailability and brain penetration characteristics. Alpha-GPC offers superior brain bioavailability with 40% choline content by weight, while CDP-choline provides additional neuroprotective benefits through its cytidine component. Phosphatidylcholine provides sustained release characteristics through its incorporation into cellular membranes, offering unique benefits for long-term brain health.
How Much Choline Is Recommended for Desired Effects?
Alpha-GPC supplementation demonstrates optimal cognitive enhancement effects at doses ranging from 300-600mg daily, divided into morning and afternoon administrations. CDP-choline requires doses of 250-750mg daily for optimal cognitive benefits, with enhanced effects noted in combination with racetam compounds. Choline bitartrate supplementation necessitates higher doses of 1000-2000mg daily due to lower brain bioavailability, though still providing significant cognitive benefits through sustained blood choline elevation.
Pharmacokinetics of Choline
Choline absorption occurs through carrier-mediated transport in the small intestine, with subsequent distribution throughout body tissues via specific choline transporters. Brain uptake involves dedicated high-affinity choline transporters at the blood-brain barrier, ensuring adequate supply for acetylcholine synthesis and membrane phospholipid production. Elimination occurs through multiple pathways including oxidation to betaine and incorporation into phospholipids.[7]
How Is Choline Absorbed, Metabolized, and Excreted in the Body?
Intestinal absorption of choline involves both sodium-dependent and independent transport mechanisms, with peak plasma levels occurring within 1-2 hours of ingestion. Metabolism proceeds through multiple pathways including acetylation for neurotransmitter synthesis, phosphorylation for membrane phospholipid production, and oxidation to betaine for methylation processes. Excretion of unmetabolized choline occurs primarily through renal pathways, while metabolized forms undergo various tissue incorporation processes.
Tolerance and Dependency Issues with Choline
Choline supplementation maintains consistent effectiveness without developing traditional tolerance patterns due to its role as an essential nutrient rather than a receptor-dependent compound. Homeostatic mechanisms regulate choline utilization and storage, preventing development of physical dependency while maintaining optimal cognitive function. Regular monitoring of cognitive response patterns ensures continued supplementation efficacy.
Can Users Develop Tolerance to Choline?
The body's response to choline supplementation remains stable over time due to complex regulatory mechanisms controlling acetylcholine synthesis and membrane phospholipid production. Physiological adaptation mechanisms prevent development of tolerance while maintaining optimal cholinergic function. Long-term supplementation benefits depend on maintaining appropriate dosing within individual therapeutic windows rather than dose escalation.
Interactions and Synergies: Choline Combinations
Racetam compounds synergize significantly with choline through increased acetylcholine utilization and enhanced receptor sensitivity. B-vitamins, particularly B6, B12, and folate, support choline metabolism through optimization of methylation pathways and neurotransmitter synthesis. Omega-3 fatty acids enhance choline incorporation into neural membranes, optimizing synaptic function and signal transduction.
What Substances Interact with Choline?
Anticholinergic medications directly oppose choline's cognitive enhancement effects through competitive receptor inhibition. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors potentiate choline's effects through reduced acetylcholine breakdown, requiring careful dose adjustment. Iron status affects choline utilization through its role in neurotransmitter synthesis and methylation processes.
What Are the Most Effective Choline Stacks?
Optimal choline stacks incorporate racetams (piracetam 1600-4800mg or oxiracetam 750-1500mg) with alpha-GPC (300-600mg) or CDP-choline (250-500mg) for enhanced cognitive effects. B-vitamin complex supplementation (including methylcobalamin B12 1000mcg, P5P B6 50mg, and methylfolate 800mcg) supports choline metabolism and utilization. Uridine monophosphate (250-500mg) enhances choline's effects on membrane phospholipid synthesis and synaptic plasticity.
Exploring Alternatives to Choline
Cholinergic compounds offer alternative pathways for enhancing cognitive function through modulation of acetylcholine signaling and neural membrane function. Natural and synthetic alternatives target similar cognitive enhancement pathways while providing complementary benefits through distinct mechanisms of action. Understanding these alternatives enables informed decisions about cognitive enhancement strategies based on individual needs and response patterns.
What Are Viable Alternatives to Choline?
Huperzine A provides cholinergic enhancement through acetylcholinesterase inhibition, offering sustained cognitive benefits with doses of 50-200mcg daily. Galantamine and vinpocetine enhance cholinergic function through distinct mechanisms, including nicotinic receptor modulation and cerebral blood flow enhancement. Lion's Mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) and Bacopa monnieri provide alternative approaches to cognitive enhancement through NGF production and cholinergic system modulation.
Insights from Scientific Research on Choline
Studies demonstrate choline's impact on brain structure and function through enhanced membrane phospholipid synthesis and cholinergic neurotransmission. Cognitive testing reveals significant improvements in memory formation, attention span, and information processing speed following choline supplementation. Longitudinal research confirms the importance of maintaining optimal choline status for cognitive development and performance throughout the lifespan.[8]
What Have Animal and Human Studies Revealed About Choline?
Research models demonstrate choline's fundamental role in neurodevelopment through regulation of stem cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation. Controlled trials confirm cognitive enhancement effects in both young and aging populations, with particularly robust improvements in memory and attention tasks. Mechanistic studies reveal detailed molecular pathways through which choline influences synaptic plasticity and neural circuit function.[9]
Evaluating the Value of Choline for Cognitive Enhancement
Regular choline supplementation offers significant cognitive benefits through enhancement of cholinergic function and neural membrane integrity. The compound's comprehensive impact on brain function, combined with its essential role in neurodevelopment, provides compelling evidence for its value in cognitive enhancement protocols. Cost-effectiveness analysis supports choline supplementation as a primary intervention for cognitive optimization.
Is Investing in Choline a Good Decision for Cognitive Enhancement?
Investment in choline supplementation provides substantial returns in cognitive performance through its fundamental role in brain function and development. The compound's established safety profile, widespread availability, and moderate cost create an attractive risk-benefit ratio for cognitive enhancement purposes. Regular monitoring ensures optimal outcomes while minimizing potential risks, making choline supplementation a sound investment in cognitive optimization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Choline
How Long Does It Take for Choline to Kick In?
Initial effects of choline supplementation become apparent within 30-60 minutes of administration, particularly with highly bioavailable forms like alpha-GPC. Cognitive enhancement effects develop fully over 2-3 weeks of consistent supplementation as cholinergic function optimizes. Individual response variations depend on baseline choline status, form of supplementation, and overall nutritional status.
How Long Does the Effect of Choline Last?
Choline's cognitive enhancement effects maintain active duration of 4-6 hours with alpha-GPC or CDP-choline supplementation. The compound's incorporation into membrane phospholipids provides sustained benefits beyond acute effects through improved neural membrane function. Regular supplementation establishes stable cognitive enhancement through maintained optimal cholinergic function.
Is Choline Legal?
Choline maintains unrestricted legal status globally as an essential nutrient critical for human health and development. Regulatory frameworks classify choline supplements as dietary supplements, ensuring widespread availability through established commercial channels. Manufacturing standards and quality control measures guarantee supplement safety and potency within legal guidelines.
Is Choline FDA-Approved?
The FDA recognizes choline as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in dietary supplements and fortified foods based on extensive safety data. Regulatory oversight ensures consistent product quality through Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines while maintaining appropriate labeling standards. Supplemental choline products undergo regular monitoring for compliance with established safety and quality parameters.
Conclusion
Choline supplementation represents a fundamental approach to cognitive enhancement through its essential role in acetylcholine synthesis and neural membrane function. The compound's comprehensive effects on brain function, combined with its excellent safety profile and cost-effectiveness, position it as a valuable tool for cognitive optimization. Careful attention to dosing, form selection, and individual response patterns maximizes benefits while maintaining optimal cholinergic function, making choline supplementation a cornerstone of evidence-based cognitive enhancement strategies.
- Sheard, N F, and S H Zeisel. “Choline: an essential dietary nutrient?.” Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.) vol. 5,1 (1989): 1-5. ↑
- López-Sobaler, Ana María et al. “Importancia de la colina en la función cognitiva” [Importance of choline in cognitive function]. Nutricion hospitalaria vol. 37,Spec No2 (2021): 18-23. doi:10.20960/nh.03351 ↑
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Military Nutrition Research; Marriott BM, editor. Food Components to Enhance Performance: An Evaluation of Potential Performance-Enhancing Food Components for Operational Rations. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 1994. 19, "Choline: Human Requirements and Effects on Human Performance." Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209047/ ↑
- Kansakar, Urna et al. “Choline supplements: An update.” Frontiers in endocrinology vol. 14 1148166. 7 Mar. 2023, doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1148166 ↑
- Liu, Lu et al. “Choline Intake Correlates with Cognitive Performance among Elder Adults in the United States.” Behavioural neurology vol. 2021 2962245. 29 Oct. 2021, doi:10.1155/2021/2962245 ↑
- Wood, J L, and R G Allison. “Effects of consumption of choline and lecithin on neurological and cardiovascular systems.” Federation proceedings vol. 41,14 (1982): 3015-21. ↑
- Buchman, A L et al. “Choline pharmacokinetics during intermittent intravenous choline infusion in human subjects.” Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics vol. 55,3 (1994): 277-83. doi:10.1038/clpt.1994.28 ↑
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutrition, Trauma, and the Brain; Erdman J, Oria M, Pillsbury L, editors. "Nutrition and Traumatic Brain Injury: Improving Acute and Subacute Health Outcomes in Military Personnel." Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2011. 9, Choline. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209327/ ↑
- Świątkiewicz, Maciej, and Paweł Grieb. “Citicoline for Supporting Memory in Aging Humans.” Aging and disease vol. 14,4 1184-1195. 1 Aug. 2023, doi:10.14336/AD.2022.0913 ↑
