Choline L-Bitartrate: Uses, Side Effects, Benefits & Where to Buy (2024)
Choline is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including neurotransmitter synthesis, cell membrane structure, and lipid metabolism. Choline bitartrate is a popular supplemental form of choline that has gained attention for its potential cognitive-enhancing effects and health benefits. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of choline bitartrate, exploring its chemical composition, mechanisms of action, potential benefits, dosage recommendations, and safety considerations.
By understanding the science behind choline bitartrate and its role in supporting brain function and overall health, readers can make informed decisions about whether to incorporate this supplement into their dietary regimen.
What Is Choline L-Bitartrate and Its Chemical Composition?
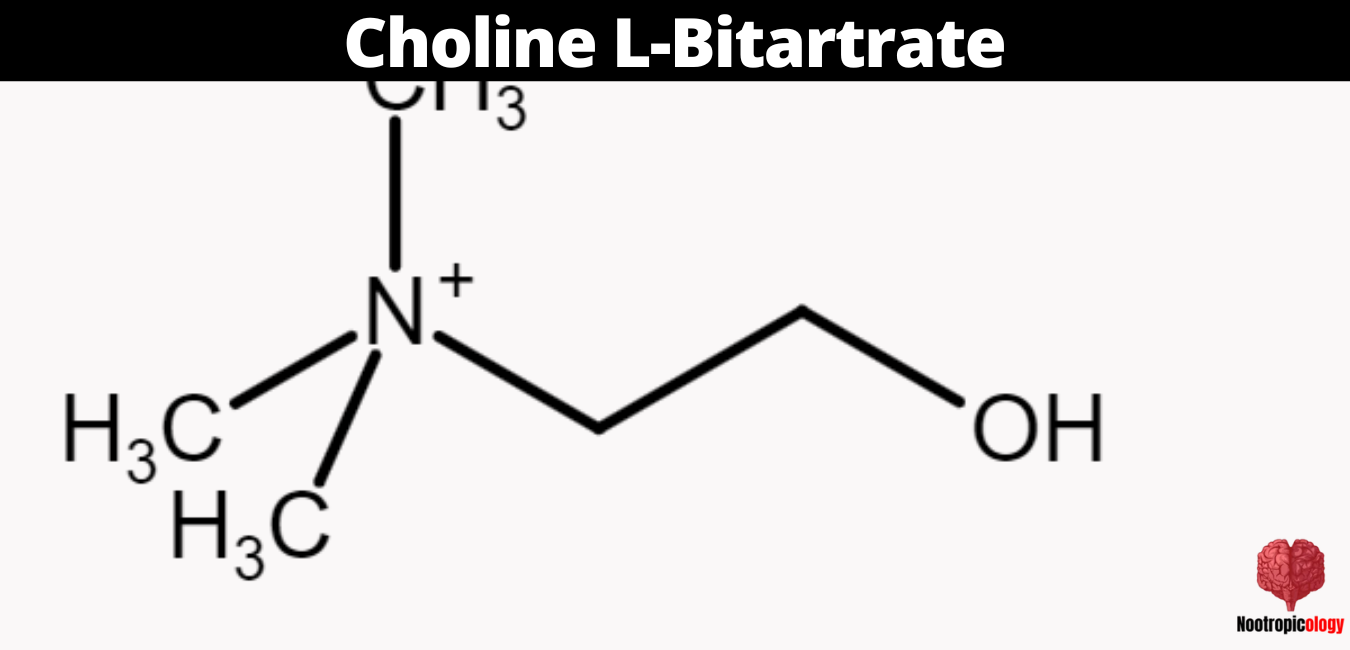

Choline bitartrate is an organic compound that is a salt of choline and tartaric acid. It is produced by the chemical reaction of trimethylamine with ethylene oxide and water, followed by a reaction with tartaric acid. Choline bitartrate has the molecular formula C9H19NO7 and a molecular weight of 253.25.
| CAS Number | 87-67-2 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.604 |
| UNII | 6K2W7T9V6Y |
| Chemical formula | C₉H₁₉NO₇ |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Non-isomeric |
| PubChem CID | 6900 |
| Molar mass | 253.251 g·mol⁻¹ |
What Is the Origin of Choline L-Bitartrate?
Choline bitartrate is produced by the chemical reaction of trimethylamine with ethylene oxide and water, followed by a reaction with tartaric acid. This process involves the formation of the choline cation from trimethylamine and ethylene oxide, which then combines with the bitartrate anion derived from tartaric acid to form the final compound. Choline bitartrate is a synthetic form of choline, which is found naturally in many food sources, particularly in animal-based products such as poultry, fish, dairy, and eggs.
What Is the Chemical Structure of Choline L-Bitartrate?
Choline bitartrate contains quaternary ammonium cations (2-hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+) and bitartrate anions (HOOC−CH(OH)−CH(OH)−COO−). The bitartrate anion is chiral and the choline cation has three methyl groups and one 2-hydroxyethyl group attached to the nitrogen. Its chemical structure can be represented as [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+HOOC−CH(OH)−CH(OH)−COO−.
How Does Choline L-Bitartrate Enhance Cognitive Function?
Choline bitartrate provides choline, an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in cognitive performance and overall brain health. By increasing acetylcholine levels, choline bitartrate can improve memory formation, attention, learning, and overall cognitive function.[1]
What Are the Biochemical Processes Influenced by Choline L-Bitartrate?
Choline bitartrate acts as a precursor for the synthesis of acetylcholine in the brain. It efficiently crosses the blood-brain barrier and increases choline levels, which are then used to produce acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter essential for various cognitive processes. By enhancing cholinergic neurotransmission, choline bitartrate can improve communication between neurons and support overall brain function.
What Are the Primary Uses and Benefits of Choline L-Bitartrate?
Choline bitartrate is commonly used as a dietary supplement to ensure adequate choline intake. It may help reduce the risk of choline deficiency which can lead to liver damage, muscle damage, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Choline supplementation during pregnancy is important for proper fetal brain development and reducing the risk of certain birth defects.[2]
How Does Choline L-Bitartrate Benefit Cognitive Disorders?
Some research suggests choline may play a role in treating or preventing certain neurological disorders like dementia, Alzheimer's disease, and bipolar disorder, although evidence is mixed. Choline bitartrate provides choline which is needed to produce acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory, mood, and muscle control. However, more studies are needed to confirm the cognitive benefits of choline supplementation in various neurological conditions.[3]
How Can Choline L-Bitartrate Improve Cognitive Performance in Healthy Individuals?
Choline bitartrate supplementation may improve memory function and brain development, but research findings are inconsistent. Some observational studies have linked higher choline intake with better cognitive performance, while other clinical trials found no significant benefits from choline supplements on cognition in healthy adults. The relationship between choline and cognitive function requires further investigation.
User Experiences and Reviews of Choline L-Bitartrate
According to reviews on various nootropic vendors websites, many users report positive experiences with choline bitartrate supplements, noting improvements in memory, focus, and mental clarity. The reviews often mention that it mixes well in water and is easy to take without causing digestive discomfort. Some individuals combine choline bitartrate with other nootropics like caffeine or racetams for synergistic cognitive benefits.
What Do Personal Experiences and Reddit Discussions Reveal About Choline L-Bitartrate?
Many Reddit users report positive experiences with choline bitartrate supplements, noting improvements in memory, focus, and mental clarity. Some individuals combine choline bitartrate with other nootropics like caffeine or racetams for synergistic cognitive benefits. However, a few users did not notice any significant effects from choline supplementation on their cognitive performance.
My Personal Choline L-Bitartrate Experience and Results
I have been taking choline bitartrate supplements for several months and have noticed a significant improvement in my memory and mental sharpness. I find that it helps me stay focused and alert throughout the day, especially when combined with my morning coffee. The supplement is easy to take and has not caused any digestive discomfort or other side effects.
How Does Choline L-Bitartrate Feel and What Results Were Observed?
Taking choline bitartrate has made me feel more mentally clear and sharp, with improved ability to recall information and stay focused on tasks. I have observed better verbal fluency and an increased capacity to process complex information quickly. The effects are subtle but noticeable, and I feel that my overall cognitive performance has improved since starting the supplement.
Practical Aspects of Acquiring Choline L-Bitartrate
Choline bitartrate supplements are widely available online and in health food stores. It is important to choose a reputable brand and ensure that the product is pure and free from contaminants. Choline bitartrate is generally affordable and can be purchased in powder or capsule form for easy consumption. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Understanding Choline L-Bitartrate's Side Effects and Safety Profile
Choline bitartrate is generally considered safe when consumed in recommended doses. However, it is important to be aware of potential side effects and safety considerations before starting supplementation. While most people tolerate choline bitartrate well, some may experience mild adverse effects, particularly at high doses.
What Are the Known Short-Term and Long-Term Side Effects?
The most common short-term side effects of choline bitartrate include digestive discomfort, such as nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Some people may also experience headaches, sweating, or a fishy body odor when taking high doses of choline supplements. These side effects are usually mild and subside when the dosage is reduced or discontinued.
Long-term safety data on choline bitartrate supplementation is limited. However, studies suggest that prolonged high intake of choline may be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease due to the formation of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) in the gut. More research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of choline supplementation.[4]
What Are the Major Drug Interactions with Choline L-Bitartrate?
Choline bitartrate has no known clinically significant drug interactions. However, it may interact with certain medications that affect cholinergic neurotransmission, such as anticholinergics and cholinesterase inhibitors. These interactions could potentially enhance or reduce the effects of choline on the body.
Administration and Dosage Guidelines for Choline L-Bitartrate
When considering choline bitartrate supplementation, it is important to understand the proper administration and dosage guidelines to ensure safety and effectiveness. The recommended dosage may vary depending on individual factors such as age, sex, and health status. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
What Are the Different Forms and Methods of Taking Choline L-Bitartrate?
Choline bitartrate supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powder. Capsules and tablets are the most convenient and commonly used forms, as they provide a pre-measured dose and are easy to swallow. Choline bitartrate powder can be mixed with water or other beverages for those who prefer a customizable dose or have difficulty swallowing pills.
How Much Choline L-Bitartrate Is Recommended for Desired Effects?
The recommended daily intake of choline varies by age, sex, and life stage. For adults, the Adequate Intake (AI) for choline is 425 mg/day for women and 550 mg/day for men. Pregnant and lactating women require higher amounts, with an AI of 450 mg/day and 550 mg/day, respectively. When using choline bitartrate supplements, it is generally recommended to start with a lower dose of 250-500 mg per day and gradually increase as needed, not exceeding the tolerable upper intake level (UL) of 3,500 mg per day for adults.
Pharmacokinetics of Choline L-Bitartrate
Choline bitartrate is rapidly absorbed in the small intestine after oral administration. Once absorbed, it is metabolized in the liver to form phosphatidylcholine, a key component of cell membranes. Choline is then distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in the brain, liver, and kidneys. Excess choline is excreted in the urine, primarily as trimethylamine oxide (TMAO).
The bioavailability of choline from choline bitartrate supplements is estimated to be around 40-60%. Peak plasma concentrations of choline are typically reached within 1-2 hours after oral ingestion. The half-life of choline in the body is relatively short, ranging from 1-4 hours, which suggests that regular intake is necessary to maintain optimal levels.
How Is Choline L-Bitartrate Absorbed, Metabolized, and Excreted in the Body?
Choline bitartrate is rapidly absorbed in the small intestine after oral administration. Once absorbed, it is metabolized in the liver to form phosphatidylcholine, a key component of cell membranes. Choline is then distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in the brain, liver, and kidneys. Excess choline is excreted in the urine, primarily as trimethylamine oxide (TMAO).
Tolerance and Dependency Issues with Choline L-Bitartrate
When considering long-term use of choline bitartrate supplements, it is important to understand potential tolerance and dependency issues. While choline is an essential nutrient and generally considered safe, some concerns have been raised regarding the development of tolerance and potential withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation.
Can Users Develop Tolerance to Choline L-Bitartrate?
Current research suggests that tolerance to choline bitartrate's cognitive-enhancing effects is unlikely to develop with regular use at recommended doses. Unlike some other nootropic substances, choline does not appear to lead to diminished responsiveness over time. However, individual experiences may vary, and more long-term studies are needed to fully understand the potential for tolerance development. It is important to note that choline bitartrate is not known to cause physical dependence or addiction.
Interactions and Synergies: Choline L-Bitartrate Combinations
Choline bitartrate may interact with certain substances, potentially enhancing or altering their effects. It is important to be aware of these interactions to ensure safety and optimize the desired outcomes of supplementation. Always consult with a healthcare professional before combining choline bitartrate with other supplements or medications.
What Substances Interact with Choline L-Bitartrate?
One well-known synergistic combination is choline bitartrate with racetam-class nootropics, such as piracetam or aniracetam. These compounds work together to increase acetylcholine levels in the brain, leading to improved cognitive performance. Choline bitartrate may also interact with other supplements and medications that affect cholinergic neurotransmission, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., donepezil) or anticholinergic drugs (e.g., scopolamine).
What Are the Most Effective Choline L-Bitartrate Stacks?
Choline bitartrate is often stacked with racetam nootropics like piracetam or aniracetam to enhance their cognitive effects. The combination of choline bitartrate and racetam can synergistically increase acetylcholine levels in the brain, leading to improved memory, focus, and learning. Some users also report positive results when combining choline bitartrate with caffeine or other stimulants for increased mental energy and alertness.
Exploring Alternatives to Choline L-Bitartrate
While choline bitartrate is a popular and effective source of choline, some individuals may be interested in exploring alternative options. These alternatives may offer different benefits, bioavailability, or overall effectiveness compared to choline bitartrate. It is important to consider individual needs and preferences when selecting a choline supplement.
What Are Viable Alternatives to Choline L-Bitartrate?
Two notable alternatives to choline bitartrate are CDP-choline (citicoline) and alpha-GPC. CDP-choline is a more bioavailable form of choline that has been shown to effectively increase acetylcholine levels and support brain health. Alpha-GPC is another highly bioavailable choline source that has been studied for its potential cognitive-enhancing effects and neuroprotective properties. Other choline-containing supplements include phosphatidylcholine, choline citrate, and choline chloride. However, these forms may have lower bioavailability or less pronounced cognitive effects compared to CDP-choline and alpha-GPC.
Insights from Scientific Research on Choline L-Bitartrate
Although choline bitartrate is a common ingredient in many nootropic supplements, scientific research on its cognitive effects is limited. Some studies suggest that choline bitartrate supplementation may improve memory and attention in healthy individuals, but the evidence is not conclusive. More research is needed to fully understand the potential nootropic benefits of choline bitartrate and to determine optimal dosing strategies.[5]
What Have Animal and Human Studies Revealed About Choline L-Bitartrate?
Animal studies suggest that choline supplementation can improve memory performance and learning. However, human studies have shown mixed results regarding the cognitive effects of choline L-bitartrate.[6] While some research indicates potential benefits for memory and attention, particularly in older adults or those with cognitive impairments, other studies have found no significant effects on cognitive performance in healthy young individuals.
Evaluating the Value of Choline L-Bitartrate for Cognitive Enhancement
When considering choline L-bitartrate for cognitive enhancement, it is important to weigh the potential benefits against the cost and effort required. While choline L-bitartrate may offer some advantages, such as improved memory and attention in certain populations, the overall value of this supplement for cognitive enhancement may vary depending on individual circumstances and goals.
Is Investing in Choline L-Bitartrate a Good Decision for Cognitive Enhancement?
For healthy individuals seeking a cognitive boost, investing in choline L-bitartrate may not provide significant returns. The evidence for its effectiveness in enhancing cognitive performance in healthy populations is limited and inconsistent. However, for older adults or those with cognitive impairments, choline L-bitartrate supplementation may be a more valuable investment, as some studies suggest potential benefits in these groups.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Choline L-Bitartrate
Your Choline L-Bitartrate questions are answered below.
How Long Does It Take for Choline L-Bitartrate to Kick In?
The onset of action for choline bitartrate can vary depending on individual factors such as age, weight, and overall health. Generally, it is absorbed quickly and can reach peak plasma levels within one to two hours after oral administration. However, the noticeable effects on cognitive function may take longer to manifest, possibly several days to weeks of consistent supplementation.
How Long Does the Effect of Choline L-Bitartrate Last?
The duration of choline bitartrate's effects can also vary between individuals. Once absorbed, choline levels in the body typically remain elevated for several hours before gradually returning to baseline. The half-life of choline in the body is estimated to be around 1-4 hours. However, the cognitive benefits of choline supplementation may persist for a longer period, especially with regular use.
What Does Choline L-Bitartrate Taste Like?
Choline bitartrate has a slightly bitter and sour taste due to the presence of bitartrate. The taste is often described as tart or acidic, similar to other compounds containing tartaric acid. Some users may find the taste unpleasant, especially when consuming choline bitartrate powder directly. Capsule or tablet forms can help mask the taste for those who are sensitive to it.
Is Choline L-Bitartrate Legal?
Yes, choline bitartrate is legal and widely available as a dietary supplement in most countries, including the United States. It is not considered a controlled substance and can be purchased without a prescription. However, it is always advisable to check your local laws and regulations regarding the purchase and use of dietary supplements.
Is Choline L-Bitartrate FDA-Approved?
Choline bitartrate is not an FDA-approved medication, as it is classified as a dietary supplement. The FDA does not require dietary supplements to undergo the same rigorous testing and approval process as prescription drugs. However, the FDA does regulate dietary supplements to ensure they are safe and properly labeled. Choline bitartrate is considered generally safe when used as directed.
What is Choline Bitartrate Toxicity?
Choline bitartrate is generally safe when consumed in recommended doses. However, excessive intake of choline can lead to toxicity symptoms such as fishy body odor, gastrointestinal distress, sweating, and hypotension. The tolerable upper intake level (UL) for choline is 3,500 mg per day for adults. Consuming choline bitartrate in doses exceeding the UL may increase the risk of adverse effects.
What Is the Difference Between Phosphatidylcholine and Choline Bitartrate?
Phosphatidylcholine is a phospholipid that contains choline as a structural component, while choline bitartrate is a salt form of choline. Phosphatidylcholine is found naturally in cell membranes and is important for their integrity and function. Choline bitartrate, on the other hand, is a supplemental form of choline that is used to increase choline levels in the body.
What Is the Difference Between Choline Bitartrate and Choline Citrate?
Choline bitartrate and choline citrate are both salt forms of choline, but they differ in the acid used to stabilize the choline molecule. Choline bitartrate is formed by combining choline with tartaric acid, while choline citrate is formed by combining choline with citric acid. Both forms are bioavailable sources of choline, but some studies suggest that choline citrate may have slightly higher bioavailability.
What Is the Difference Between Choline Bitartrate and Choline Chloride?
Choline bitartrate and choline chloride are both salt forms of choline, but they differ in the anion attached to the choline molecule. Choline bitartrate contains the bitartrate anion, while choline chloride contains the chloride anion. Choline chloride is commonly used in animal feed and is less expensive than choline bitartrate. However, choline bitartrate is more commonly used in human supplements due to its higher bioavailability.
Is Choline Bitartrate Beneficial for Hair?
Choline is important for the health of hair follicles and may play a role in preventing hair loss. Choline deficiency has been associated with hair loss in animal studies. However, there is limited research specifically on the effects of choline bitartrate supplementation on hair health in humans. More studies are needed to determine if choline bitartrate can provide significant benefits for hair growth and quality.
Is Choline Bitartrate Good for Depression?
Some studies suggest that choline supplementation may have potential benefits for depression. Choline is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters like acetylcholine and serotonin, which are important for mood regulation. However, the specific effects of choline bitartrate on depression have not been extensively studied.
What Is the Relationship Between Choline Bitartrate and Inositol?
Choline and inositol are both important nutrients for brain function and are often found together in dietary sources. Inositol is a carbohydrate that is involved in cell signaling and neurotransmitter regulation. Some studies suggest that combining choline and inositol supplements may have synergistic effects on cognitive performance and mood.
Can Choline Bitartrate Aid in Weight Loss?
Choline plays a role in lipid metabolism and may help prevent the accumulation of fat in the liver. Some studies have suggested that choline supplementation may be beneficial for weight loss and body composition. However, the specific effects of choline bitartrate on weight loss have not been extensively studied.
Can Choline Bitartrate Help With Gallstones?
Choline is involved in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine, a compound that helps solubilize cholesterol in bile and prevent the formation of gallstones. Some studies have suggested that choline supplementation may help reduce the risk of gallstones.
Can Choline Bitartrate Help Prevent Heart Disease?
Choline is involved in the regulation of homocysteine, an amino acid that has been associated with an increased risk of heart disease. Some studies have suggested that choline supplementation may help lower homocysteine levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Is Choline Bitartrate Safe During Pregnancy?
Choline is an important nutrient for fetal development, particularly for brain and spinal cord formation. The demand for choline increases during pregnancy, and some studies have suggested that choline supplementation may help reduce the risk of certain birth defects. Choline bitartrate is generally considered safe during pregnancy when consumed in recommended doses.
Can Choline Bitartrate Be Used as a Pre-workout Supplement?
Choline bitartrate is sometimes included in pre-workout supplements due to its potential cognitive-enhancing effects. Choline is involved in the synthesis of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is important for muscle contraction and focus. Some studies have suggested that choline supplementation may help improve exercise performance and delay fatigue.
- Kansakar, Urna et al. “Choline supplements: An update.” Frontiers in endocrinology vol. 14 1148166. 7 Mar. 2023, doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1148166 ↑
- Corbin, Karen D, and Steven H Zeisel. “Choline metabolism provides novel insights into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its progression.” Current opinion in gastroenterology vol. 28,2 (2012): 159-65. doi:10.1097/MOG.0b013e32834e7b4b ↑
- Aguree, Sixtus et al. “Association between choline supplementation and Alzheimer's disease risk: a systematic review protocol.” Frontiers in aging neuroscience vol. 15 1242853. 28 Aug. 2023, doi:10.3389/fnagi.2023.1242853 ↑
- Zhen, Jing et al. “The gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide and cardiovascular diseases.” Frontiers in endocrinology vol. 14 1085041. 7 Feb. 2023, doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1085041 ↑
- Tabassum, Saiqa et al. “Chronic choline supplementation improves cognitive and motor performance via modulating oxidative and neurochemical status in rats.” Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior vol. 159 (2017): 90-99. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2017.05.011 ↑
- Lippelt, D P et al. “No Acute Effects of Choline Bitartrate Food Supplements on Memory in Healthy, Young, Human Adults.” PloS one vol. 11,6 e0157714. 24 Jun. 2016, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0157714 ↑
